Python微信订餐小程序课程视频
https://edu.csdn.net/course/detail/36074
Python实战量化交易理财系统
https://edu.csdn.net/course/detail/35475作者:https://blog.csdn.net/w1570631036/p/16028174.html
目录
SearchType搜索入口:3.1 query阶段3.2 Fetch阶段3.2.1 FetchSearchPhase(对应上面的1)3.2.2 ExpandSearchPhase(对应上图的2)4.1 执行query、fetch流程
本文基于elasticsearch8.1。在es搜索中,经常会使用索引+星号,采用时间戳来进行搜索,比如aaaa-*在es中是怎么处理这类请求的呢?是对匹配的进行搜索呢还是仅仅根据时间找出索引,然后才遍历索引进行搜索。在了解其原理前先了解一些基本知识。
SearchType
QUERY_THEN_FETCH(默认):第一步,先向所有的shard发出请求,各分片只返回排序和排名相关的信息(注意,不包括文档document),然后按照各分片返回的分数进行重新排序和排名,取前size个文档。然后进行第二步,去相关的shard取document。这种方式返回的document与用户要求的size是相等的。
DFS_QUERY_THEN_FETCH:比第1种方式多了一个初始化散发(initial scatter)步骤。
为了能够深刻了解es的搜索过程,首先创建3个索引,每个索引指定一天的一条记录。
POST aaaa-16/_doc
{
"@timestamp": "2022-02-16T16:21:15.000Z",
"word":"16"
}
POST aaaa-17/_doc
{
"@timestamp": "2022-02-17T16:21:15.000Z",
"word":"17"
}
POST aaaa-18/_doc
{
"@timestamp": "2022-02-18T16:21:15.000Z",
"word":"18"
}
即可在kibana上看到3条数据
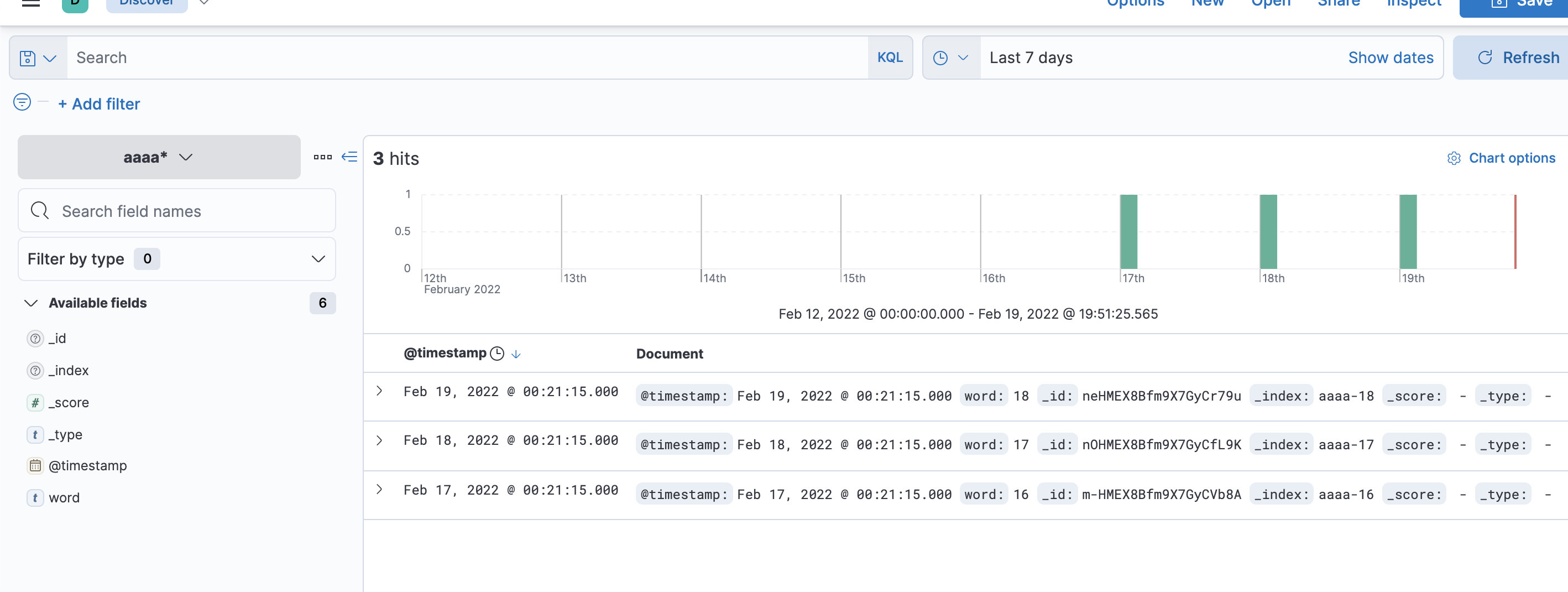
此时,假设我们用一个索引+星号来搜索,es内部的搜索是怎么样的呢?
GET aaaa*/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"@timestamp": {
"gte": "2022-02-18T10:21:15.000Z",
"lte": "2022-02-18T17:21:15.000Z"
}
}
}
}
正好命中一条记录返回。
{
"took" : 2,
"timed\_out" : false,
"\_shards" : {
"total" : 3,
"successful" : 3,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max\_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"\_index" : "aaaa-18",
"\_id" : "0zB2O38BoMIMP8QzHgdq",
"\_score" : 1.0,
"\_source" : {
"@timestamp" : "2022-02-18T16:21:15.000Z",
"word" : "18"
}
}
]
}
}
一、es的分布式搜索过程
一个搜索请求必须询问请求的索引中所有分片的某个副本来进行匹配。假设一个索引有5个主分片,每个主分片有1个副分片,共10个分片,一次搜索请求会由5个分片来共同完成,它们可能是主分片,也可能是副分片。也就是说,一次搜索请求只会命中所有分片副本中的一个。当搜索任务执行在分布式系统上时,整体流程如下图所示。图片来源Elasitcsearch源码解析与优化实战

搜索入口:
整个http请求的入口,主要使用的是Netty4HttpRequestHandler。
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
class Netty4HttpRequestHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpPipelinedRequest httpRequest) {
final Netty4HttpChannel channel = ctx.channel().attr(Netty4HttpServerTransport.HTTP\_CHANNEL\_KEY).get();
boolean success = false;
try {
serverTransport.incomingRequest(httpRequest, channel);
success = true;
} finally {
if (success == false) {
httpRequest.release();
}
}
}
}
二、初步调用流程
调用链路过程:Netty4HttpRequestHandler.channelRead0->AbstractHttpServerTransport.incomingRequest->AbstractHttpServerTransport.handleIncomingRequest->AbstractHttpServerTransport.dispatchRequest->RestController.dispatchRequest(实现了HttpServerTransport.Dispatcher)->SecurityRestFilter.handleRequest->BaseRestHandler.handleRequest->action.accept(channel)->RestCancellableNodeClient.doExecute->NodeClient.executeLocally->RequestFilterChain.proceed->TransportAction.proceed->TransportSearchAction.doExecute->TransportSearchAction.executeRequest(判断是本地执行还是远程执行)->TransportSearchAction.searchAsyncAction
协调节点的主要功能是接收请求,解析并构建目的的shard列表,然后异步发送到数据节点进行请求查询。具体就不细讲了,可按着debug的来慢慢调试。
特别注意下RestCancellableNodeClient.doExecute,从executeLocally执行所有的查询过程,并注册监听listener.onResponse(response),然后响应。
public extends ActionRequest, Response extends ActionResponse> void doExecute(...) {
...
TaskHolder taskHolder = new TaskHolder();
Task task = client.executeLocally(action, request, new ActionListener<>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(Response response) {
try {
closeListener.unregisterTask(taskHolder);
} finally {
listener.onResponse(response);
}
}
});
...
}
其次要注意的是:TransportSearchAction.searchAsyncAction才开始真正的搜索过程
private SearchPhase searchAsyncAction(...) {
...
final QueryPhaseResultConsumer queryResultConsumer = searchPhaseController.newSearchPhaseResults();
AbstractSearchAsyncAction <span class="hljs-keyword"extends SearchPhaseResult> searchAsyncAction = switch (searchRequest.searchType()) {
case DFS_QUERY_THEN_FETCH -> new SearchDfsQueryThenFetchAsyncAction(...);
case QUERY_THEN_FETCH -> new SearchQueryThenFetchAsyncAction(...);
};
return searchAsyncAction;
...
}
之后就是执行AbstractSearchAsyncAction.start,启动AbstractSearchAsyncAction.executePhase的查询动作。
此处的SearchPhase实现类为SearchQueryThenFetchAsyncAction
private void executePhase(SearchPhase phase) {
try {
phase.run();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(new ParameterizedMessage("Failed to execute [{}] while moving to [{}] phase", request, phase.getName()), e);
}
onPhaseFailure(phase, "", e);
}
}
三、协调节点
两阶段相应的实现位置:查询(Query)阶段—search.SearchQueryThenFetchAsyncAction;取回(Fetch)阶段—search.FetchSearchPhase。它们都继承自SearchPhase,如下图所示。
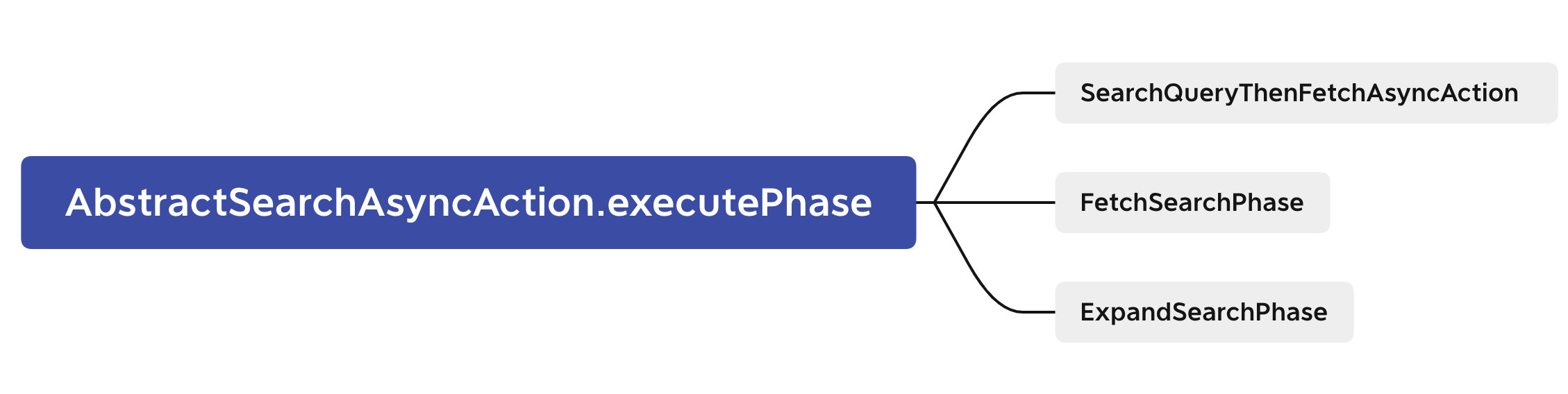
3.1 query阶段
图片来源官网,比较旧,但任然可用
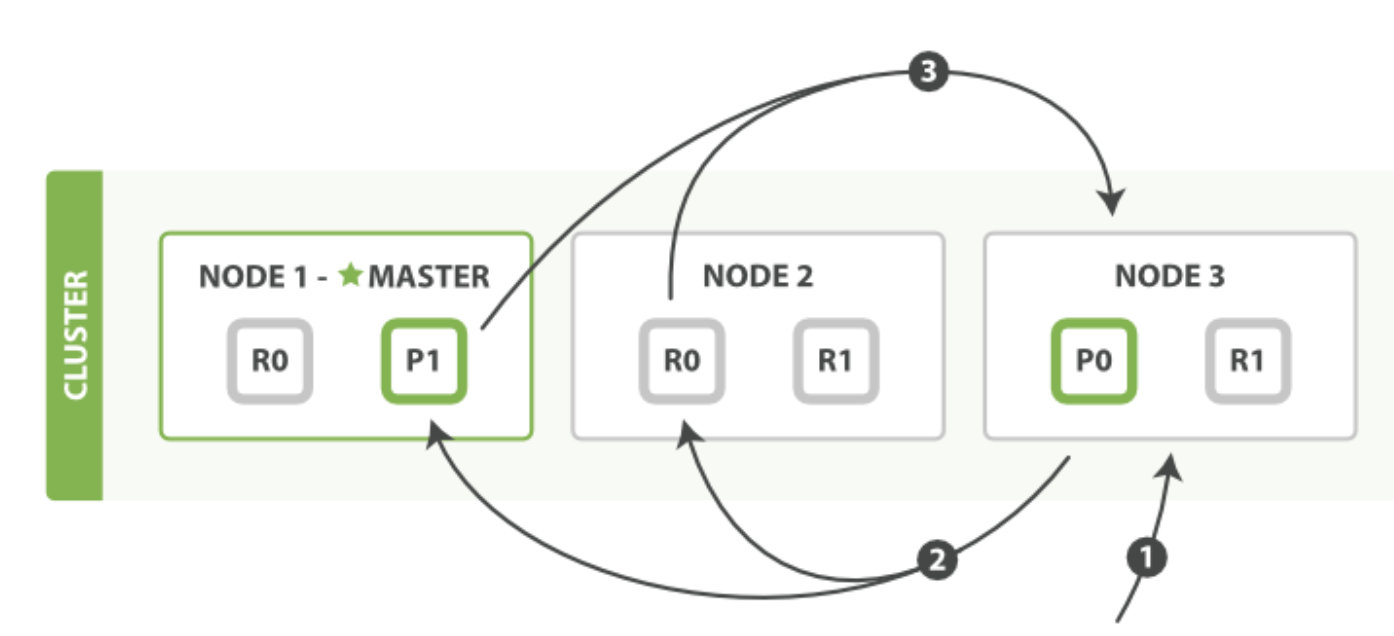
(1)客户端发送一个search请求到node3,node3创建一个大小为from,to的优先级队列。
(2)node3转发转发search请求至索引的主分片或者副本,每个分片执行查询请求,并且将结果放到一个排序之后的from、to大小的优先级队列。
(3)每个分片把文档id和排序之后的值返回给协调节点node3,node3把结果合并然后创建一个全局排序之后的结果。
在RestSearchAction#prepareRequest方法中将请求体解析为SearchRequest 数据结构:
public RestChannelConsumer prepareRequest(.. .) {
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest();
request.withContentOrSourceParamParserOrNull (parser ->
parseSearchRequest (searchRequest, request, parser, setSize));
...
}
3.1.1 构造目的shard列表
将请求涉及的本集群shard列表和远程集群的shard列表(远程集群用于跨集群访问)合并:
private void executeSearch(.. .) {
...
final GroupShardsIterator shardIterators = mergeShardsIterators(localShardIterators, remoteShardIterators);
localShardIterators = StreamSupport.stream(localShardRoutings.spliterator(), false).map(it -> {
OriginalIndices finalIndices = finalIndicesMap.get(it.shardId().getIndex().getUUID());
assert finalIndices != null;
return new SearchShardIterator(searchRequest.getLocalClusterAlias(), it.shardId(), it.getShardRoutings(), finalIndices);
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
...
}
查看结果
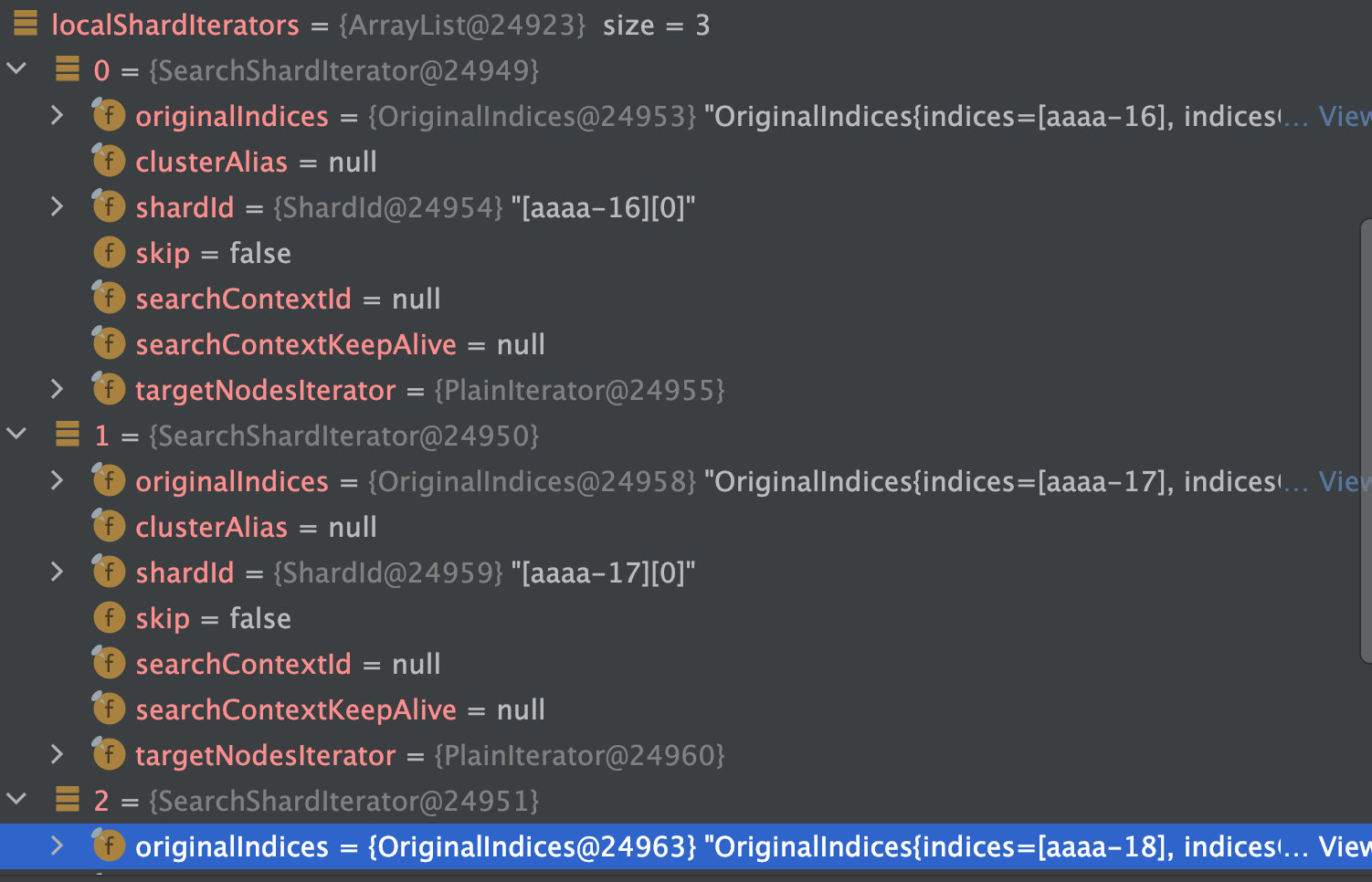
3.1.2 对所有分片进行搜索
AbstractSearchAsyncAction.run
对每个分片进行搜索查询
for (int i = 0; i < shardsIts.size(); i++) {
final SearchShardIterator shardRoutings = shardsIts.get(i);
assert shardRoutings.skip() == false;
assert shardIndexMap.containsKey(shardRoutings);
int shardIndex = shardIndexMap.get(shardRoutings);
performPhaseOnShard(shardIndex, shardRoutings, shardRoutings.nextOrNull());
}
其中shardsIts是所有aaaa*的所有索引+其中一个副本
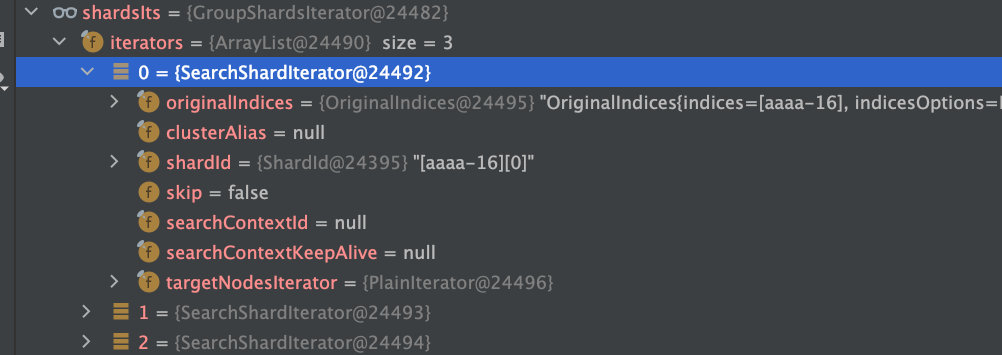
3.1.3 分片具体的搜索过程
AbstractSearchAsyncAction.performPhaseOnShard
private void performPhaseOnShard(. ..) {
executePhaseOnShard(.. .) {
//收到执行成功的回复
public void inne rOnResponse (FirstResult result) {
maybeFork (thread, () -> onShardResult (result,shardIt) );
}
//收到执行失败的回复
public void onFailure (Exception t) {
maybeFork(thread, () -> onShardFailure (shardIndex, shard, shard. currentNodeId(),shardIt, t));
}
});
}
分片结果,当前线程
//AbstractSearchAsyncAction.onShardResult
...
private void onShardResult (FirstResult result, SearchShardIterator shardIt) {
onShardSuccess(result);
success fulShardExecution(shardIt);
}
...
//AbstractSearchAsyncAction.onShardResultConsumed
private void successfulShardExecution (SearchShardIterator shardsIt) {
//计数器累加.
final int xTotalOps = totalOps.addAndGet (remainingOpsOnIterator);
//检查是否收到全部回复
if (xTotalOps == expectedTotalOps) {
onPhaseDone ();
} else if (xTota1Ops > expectedTotal0ps) {
throw new AssertionError(. ..);
}
}
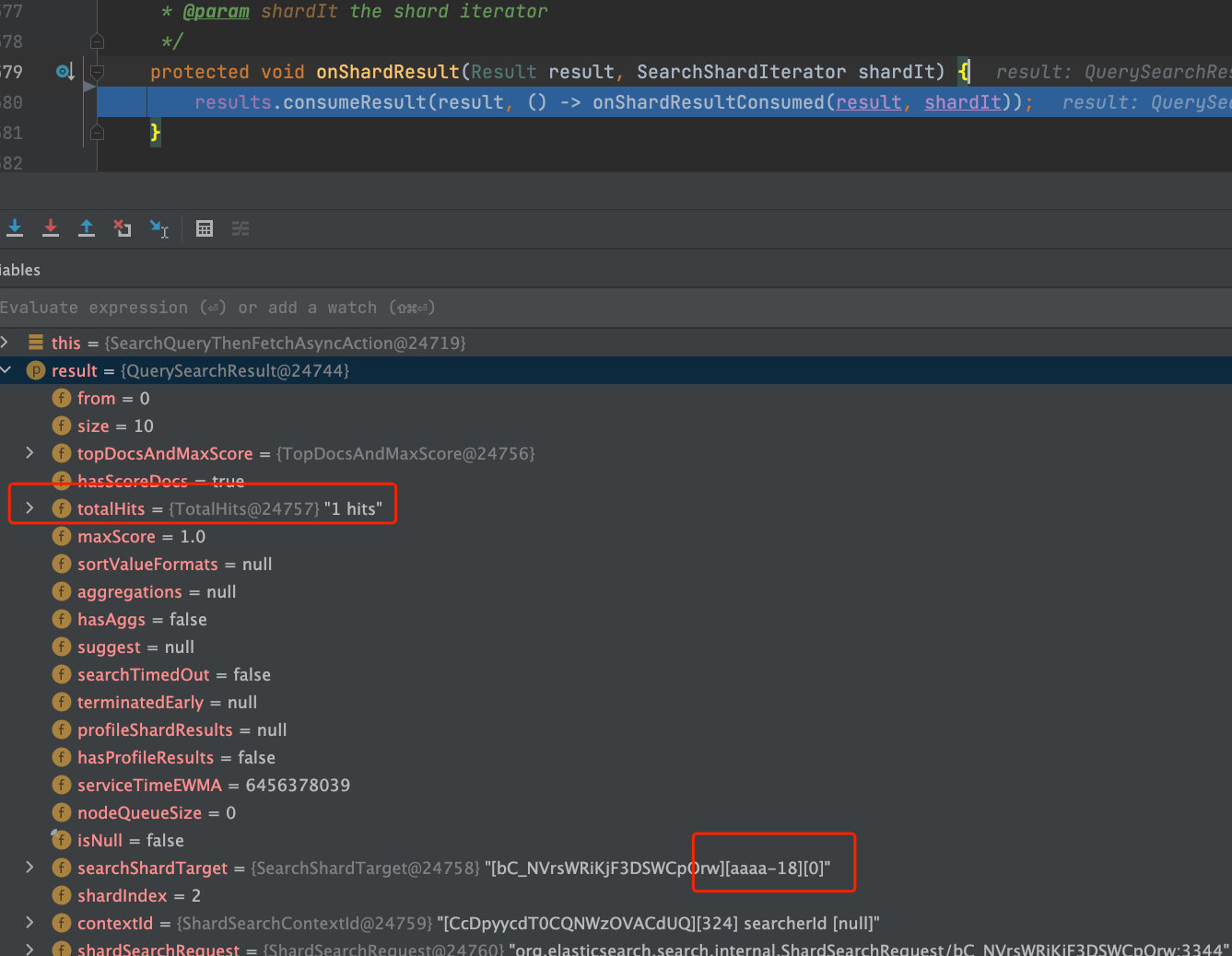
此处忽略了搜索结果totalHits为0的结果,并将结果进行累加,当xTotalOps等于expectedTotalOps时开始AbstractSearchAsyncAction.onPhaseDone再进行AbstractSearchAsyncAction.executeNextPhase取回阶段
3.2 Fetch阶段
取回阶段,图片来自官网,
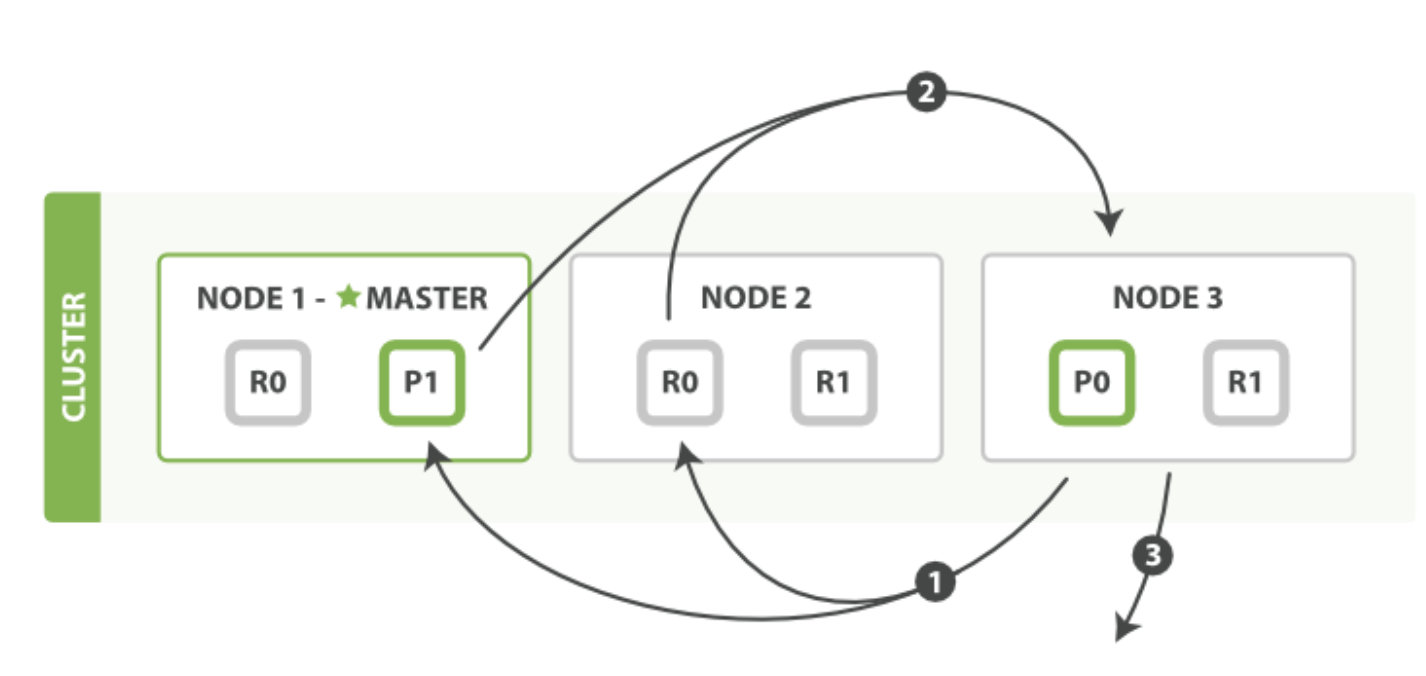
(1)各个shard 返回的只是各文档的id和排序值 IDs and sort values ,coordinate node根据这些id&sort values 构建完priority queue之后,然后把程序需要的document 的id发送mget请求去所有shard上获取对应的document
(2)各个shard将document返回给coordinate node
(3)coordinate node将合并后的document结果返回给client客户端
3.2.1 FetchSearchPhase(对应上面的1)
Query阶段的executeNextPhase方法触发Fetch阶段,Fetch阶段的起点为FetchSearchPhase#innerRun函数,从查询阶段的shard列表中遍历,跳过查询结果为空的shard,对特定目标shard执行executeFetch来获取数据,其中包括分页信息。对scroll请求的处理也在FetchSearchPhase#innerRun函数中。
private void innerRun() throws Exception {
final int numShards = context.getNumShards();
final boolean isScrollSearch = context.getRequest().scroll() != null;
final List phaseResults = queryResults.asList();
final SearchPhaseController.ReducedQueryPhase reducedQueryPhase = resultConsumer.reduce();
final boolean queryAndFetchOptimization = queryResults.length() == 1;
final Runnable finishPhase = () -> moveToNextPhase(
searchPhaseController,
queryResults,
reducedQueryPhase,
queryAndFetchOptimization ? queryResults : fetchResults.getAtomicArray()
);
for (int i = 0; i < docIdsToLoad.length; i++) {
IntArrayList entry = docIdsToLoad[i];
SearchPhaseResult queryResult = queryResults.get(i);
if (entry == null) {
if (queryResult != null) {
releaseIrrelevantSearchContext(queryResult.queryResult());
progressListener.notifyFetchResult(i);
}
counter.countDown();
}else{
executeFetch(
queryResult.getShardIndex(),
shardTarget,
counter,
fetchSearchRequest,
queryResult.queryResult(),
connection
);
}
}
}
}
再看源码:
启动一个线程来fetch
AbstractSearchAsyncAction.executePhase->FetchSearchPhase.run->FetchSearchPhase.innerRun->FetchSearchPhase.executeFetch
private void executeFetch(...) {
context.getSearchTransport()
.sendExecuteFetch(
connection,
fetchSearchRequest,
context.getTask(),
new SearchActionListener(shardTarget, shardIndex) {
@Override
public void innerOnResponse(FetchSearchResult result) {
progressListener.notifyFetchResult(shardIndex);
counter.onResult(result);
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Exception e) {
progressListener.notifyFetchFailure(shardIndex, shardTarget, e);
counter.onFailure(shardIndex, shardTarget, e);
}
}
);
}
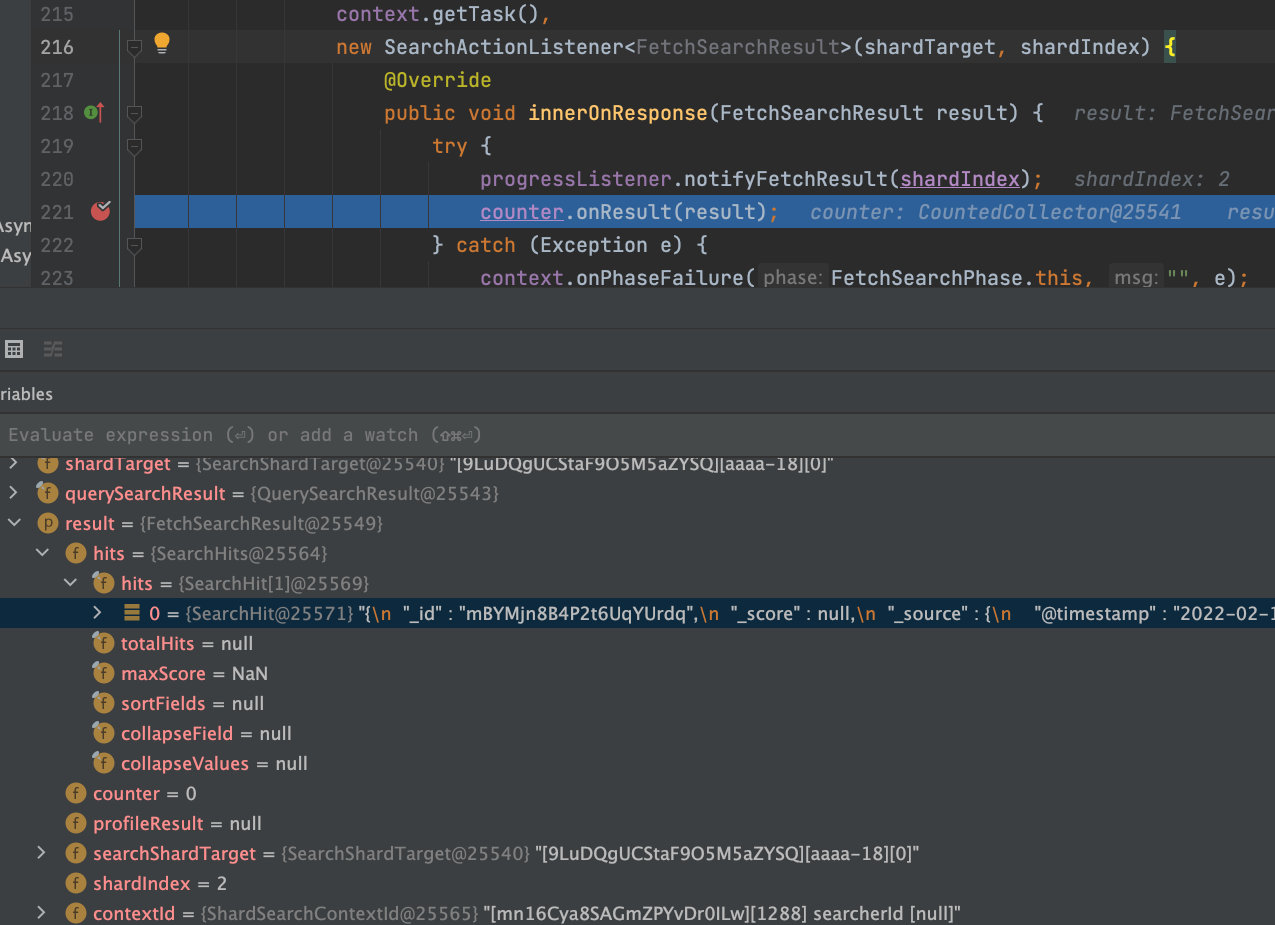
counter是一个收集器CountedCollector,onResult(result)主要是每次收到的shard数据存放,并且执行一次countDown,当所有shard数据收集完之后,然后触发一次finishPhase。
# CountedCollector.class
void countDown() {
assert counter.isCountedDown() == false : "more operations executed than specified";
if (counter.countDown()) {
onFinish.run();
}
}
moveToNextPhase方法执行下一阶段,下-阶段要执行的任务定义在FetchSearchPhase构造 函数中,主要是触发ExpandSearchPhase。
3.2.2 ExpandSearchPhase(对应上图的2)
AbstractSearchAsyncAction.executePhase->ExpandSearchPhase.run。取回阶段完成之后执行ExpandSearchPhase#run,主要判断是否启用字段折叠,根据需要实现字段折叠功能,如果没有实现字段折叠,则直接返回给客户端。
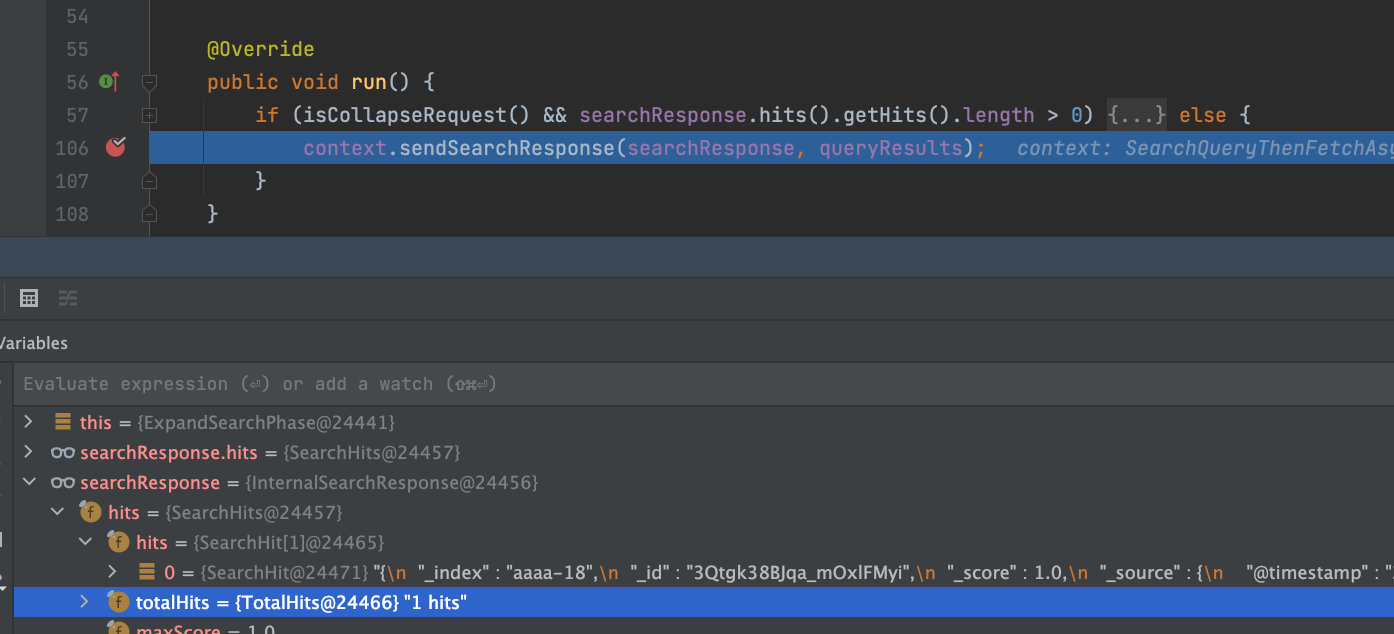
ExpandSearchPhase执行完之后回复客户端,在AbstractSearchAsyncAction.sendSearchResponse方法中实现:
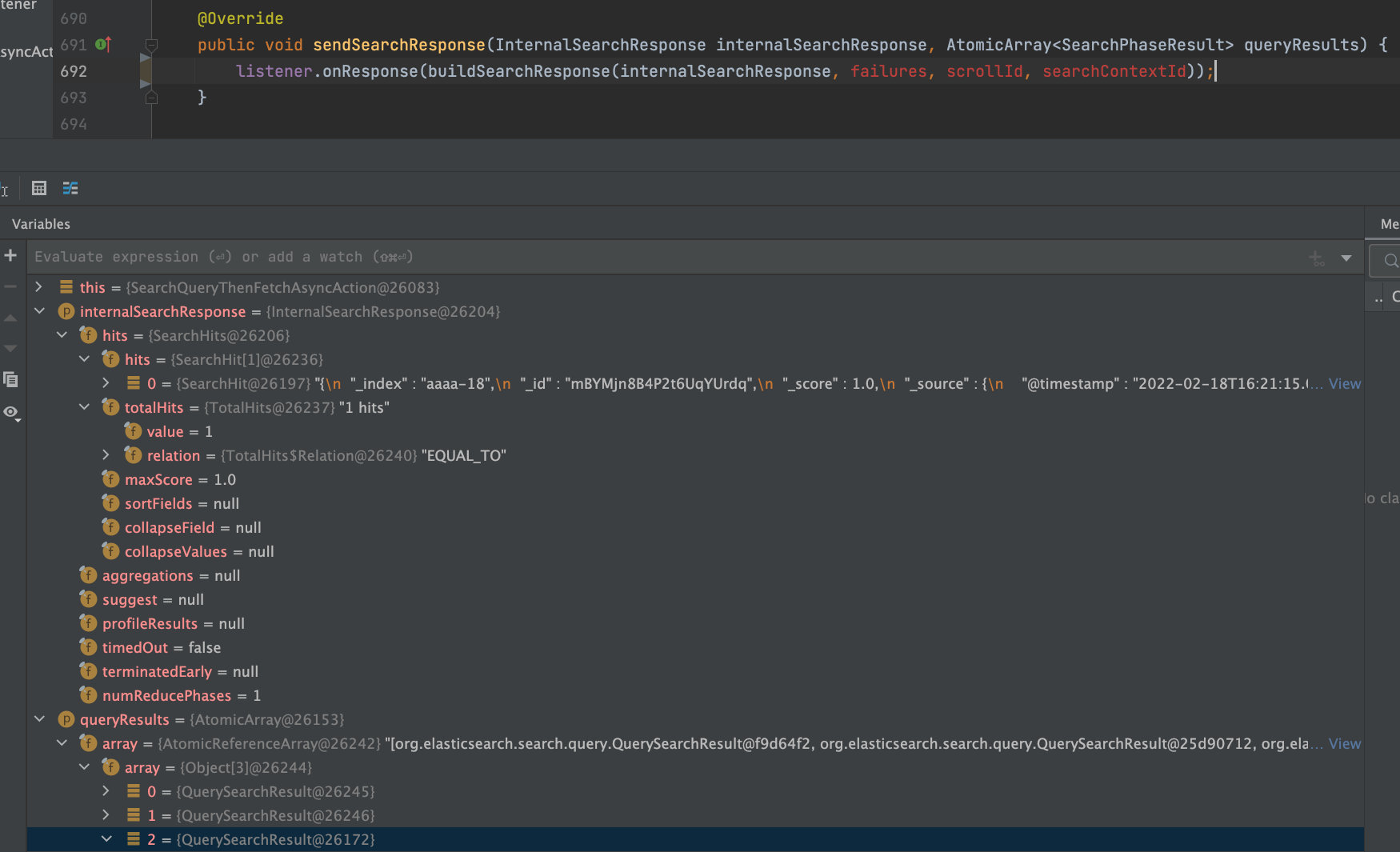
四、数据节点
4.1 执行query、fetch流程
执行本流程的线程池: search。
对各种Query请求的处理入口注册于SearchTransportService.registerRequestHandler。
public static void registerRequestHandler(TransportService transportService, SearchService searchService) {
...
transportService.registerRequestHandler(
QUERY_ACTION_NAME,
ThreadPool.Names.SAME,
ShardSearchRequest::new,
(request, channel, task) -> searchService.executeQueryPhase(
request,
(SearchShardTask) task,
new ChannelActionListener<>(channel, QUERY_ACTION_NAME, request)
)
);
...
}
4.1.1 执行query请求
# SearchService
public void executeQueryPhase(ShardSearchRequest request, SearchShardTask task, ActionListener listener) {
assert request.canReturnNullResponseIfMatchNoDocs() == false || request.numberOfShards() > 1
: "empty responses require more than one shard";
final IndexShard shard = getShard(request);
rewriteAndFetchShardRequest(shard, request, listener.delegateFailure((l, orig) -> {
ensureAfterSeqNoRefreshed(shard, orig, () -> executeQueryPhase(orig, task), l);
}));
}
其中ensureAfterSeqNoRefreshed是把request任务放到一个名为search的线程池里面执行,容量大小为1000。
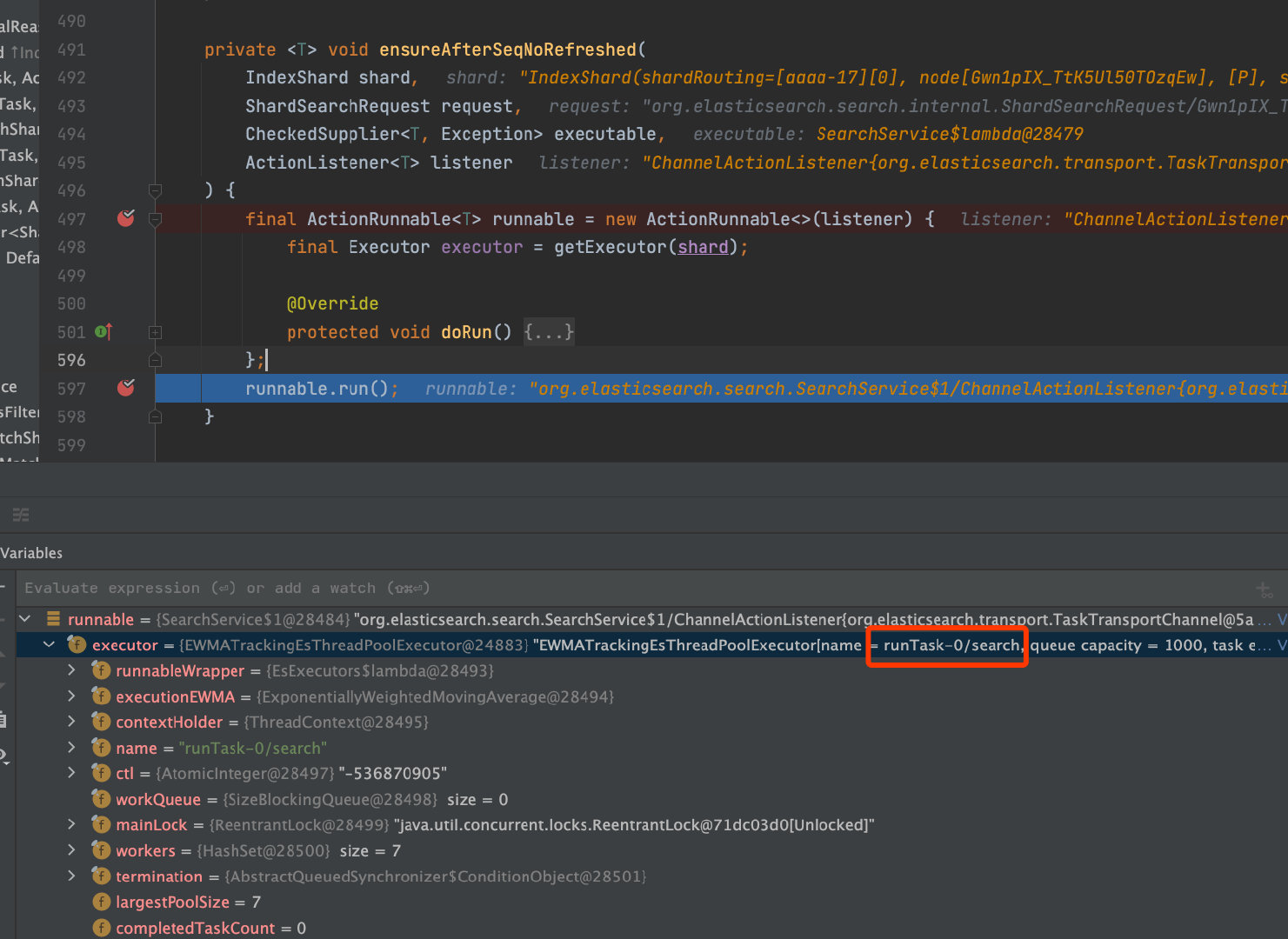
主要是用来执行SearchService.executeQueryPhase->SearchService.loadOrExecuteQueryPhase->QueryPhase.execute。核心的查询封装在queryPhase.execute(context)中,其中调用Lucene实现检索,同时实现聚合:
public void execute (SearchContext searchContext) {
aggregationPhase.preProcess (searchContext);
boolean rescore = execute ( searchContext, searchContext.searcher(), searcher::setCheckCancelled, indexSort);
if (rescore) {
rescorePhase.execute (searchContext);
suggestPhase.execute (searchContext);
aggregationPhase.execute (searchContext);
}
}
其中包含几个核心功能:
- execute(),调用Lucene、searcher.search()实现搜索
- rescorePhase,全文检索且需要打分
- suggestPhase,自动补全及纠错
- aggregationPhase,实现聚合
4.1.2 fetch流程
对各种Fetch请求的处理入口注册于SearchTransportService.registerRequestHandler。
transportService.registerRequestHandler(
QUERY_FETCH_SCROLL_ACTION_NAME,
ThreadPool.Names.SAME,
InternalScrollSearchRequest::new,
(request, channel, task) -> {
searchService.executeFetchPhase(
request,
(SearchShardTask) task,
new ChannelActionListener<>(channel, QUERY_FETCH_SCROLL_ACTION_NAME, request)
);
}
);
对Fetch响应的实现封装在SearchService.executeFetchPhase中,核心是调用fetchPhase.execute(context)。按照命中的doc取得相关数据,填充到SearchHits中,最终封装到FetchSearchResult中。
# FetchPhase
public void execute(SearchContext context) {
Profiler profiler = context.getProfilers() == null ? Profiler.NOOP : context.getProfilers().startProfilingFetchPhase();
SearchHits hits = null;
try {
//lucene构建搜索的结果
hits = buildSearchHits(context, profiler);
} finally {
ProfileResult profileResult = profiler.finish();
// Only set the shardResults if building search hits was successful
if (hits != null) {
context.fetchResult().shardResult(hits, profileResult);
}
}
}
五、数据返回
入口:RestCancellableNodeClient.doExecute
Task task = client.executeLocally主要执行查询,并使用了ActionListener来进行监听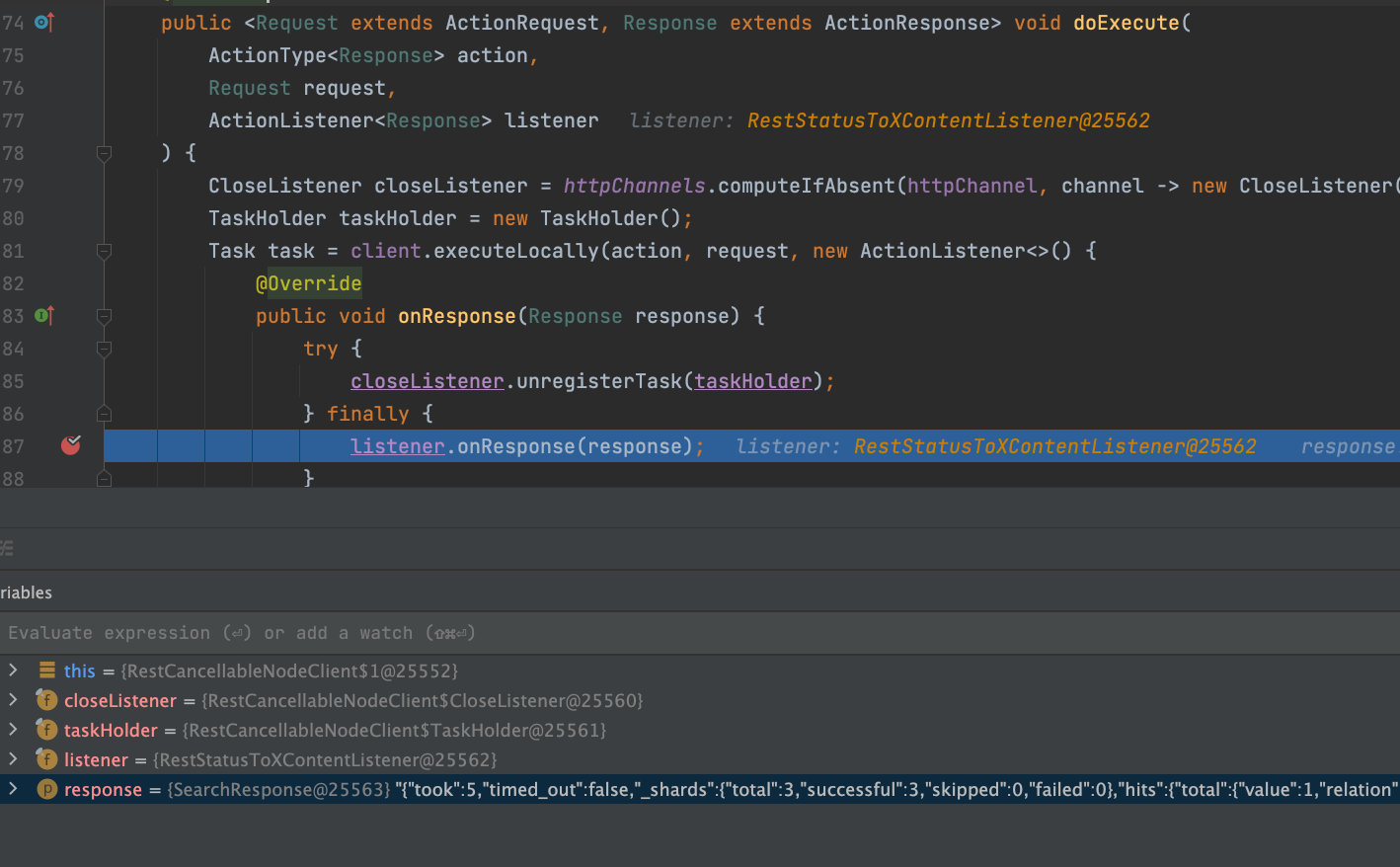
其中onResponse的调用链路如下:RestActionListener.onResponse->RestResponseListener.processResponse->RestController.sendResponse->DefaultRestChannel.sendResponse->Netty4HttpChannel.sendResponse
public void sendResponse(RestResponse restResponse) {
...
httpChannel.sendResponse(httpResponse, listener);
...
}
最后由Netty4HttpChannel.sendResponse来响应请求。
六、总结
当我们以aaaa*这样来搜索的时候,实际上查询了所有匹配以aaaa开头的索引,并且对所有的索引的分片都进行了一次Query,再然后对有结果的分片进行一次fetch,最终才能展示结果。可能觉得好奇,对所有分片都进行一次搜索,遍历分片所有的Lucene分段,会不会太过于消耗资源,因此合并Lucene分段对搜索性能有好处,这里下篇文章在讲吧。同时,聚合是发生在fetch过程中的,并不是lucene。
本文参考
- Elasitcsearch源码解析与优化实战
- Elasticsearch源码分析-搜索分析(一)
- Elasticsearch源码分析-搜索分析(二)
- Elasticsearch源码分析-搜索分析(三)
- Elasticsearch 通信模块的分析
- Elasticsearch 网络通信线程分析
转载请注明:xuhss » 【elasticsearch】搜索过程详解