文章目录
显示
Python微信订餐小程序课程视频
https://edu.csdn.net/course/detail/36074
Python实战量化交易理财系统
https://edu.csdn.net/course/detail/35475
1树的定义及相关术语
1.1 树的定义
- 树是一种非线性的数据结构,由n(n>=0)个结点组成的有限集合;
- 如果n=0,称为空树;
- 如果n>0,则:
- 有一个特定的结点被称之为根结点(root),根结点只有直接后继,没有前驱;
- 除根结点外的其他结点划分为m(m>=0)个互不相交的有限集合T0,T1...Tm-1,每一个集合又是一颗子树,并称之为根的子树。
1.2 树的特点
- 每个结点有零个或多个子结点;
- 没有父结点的结点称为根结点;每一个非根结点有且只有一个父结点;除了根结点外,每个子结点可以分为多个不相交的子树;
- 节点的数量等于边数加一;树由n 个节点 和 (n-1)条边 构成,其中n ≥ 1;
- 树或栈这种数据结构用于解决 具有完全包含关系的问题;
- 问题抽象(思维逻辑):本质上是把一个大问题分成若干个小问题,当小问题解决了,大问题自然也解决了;首先,将树中的“节点”看作“集合”,“边”看作“关系”,接着把“全集”看成是一个大问题,而“子集”看作是若干个小问题,我们只需要关注小问题的求解即可。
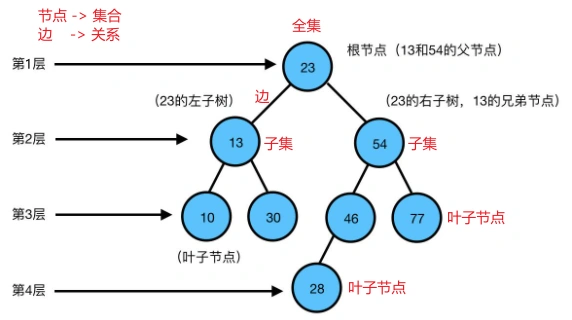
1.3 树的相关术语
- 节点深度:对任意节点x,x节点的深度表示为根节点到x节点的路径长度。所以根节点深度为0,第二层节点深度为1,以此类推;
- 节点高度:对任意节点x,叶子节点到x节点的路径长度就是节点x的高度;
- 树的深度(高度):一棵树中节点的最大深度就是树的深度,也称为树的高度;
- 度:节点的子树数目就是节点的度;
- 叶子节点 vs 分支节点:度为零的节点就是叶子节点(路径中的最后一个节点);度不为零的节点就是分支节点;
- 父节点:若一个节点含有子节点,则这个节点称为其子节点的父节点;
- 子节点:一个节点含有的子树的根节点称为该节点的子节点;
- 兄弟节点:拥有共同父节点的节点互称为兄弟节点;
- 节点的层次:从根节点开始,根节点为第一层,根的子节点为第二层,以此类推;
- 祖先:对任意节点x,从根节点到节点x的所有节点都是x的祖先(节点x也是自己的祖先)
- 后代:对任意节点x,从节点x到叶子节点的所有节点都是x的后代(节点x也是自己的后代)
- 森林:m颗互不相交的树构成的集合就是森林
- n叉树:由一个节点向外最多引出节点的数量,即当前这个节点最多向外有n个指向;
- 补充:度分为“入度”和“出度”;
- 出度:由一个节点向外指向边的数量;
- 入度:有多少条边指向一个节点的数量;树的入度为1,所以只考虑出度,即为度;
- 案例:
- 树的深度(高度):4,path = 1→4→6→8
- 节点4的深度:2,path = 1→4;节点4的高度:3,path = 8→6→4
- 节点2的度:1, =(5, );节点4的度:2,=(6, 7);叶子节点的度:0
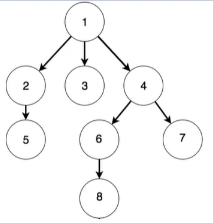
2 二叉树
2.1 定义
- 在一个树中,由一个节点向外最多引出2个节点,即当前这个节点最多向外有2个指向;
2.2 n叉树 vs 二叉树
如何定义n叉树,n是多少的问题?
- 对于n叉树中的n是一个不确定性的问题,一般计算机只能处理确定性问题,所以,我们可以将n 叉树转换为2叉树来思考;
- 由于计算机底层是基于二进制计算的,故2 叉树 与 n叉树之间可以相互转换;
- 表示方法:左孩子右兄弟表示法,又名十字链表法
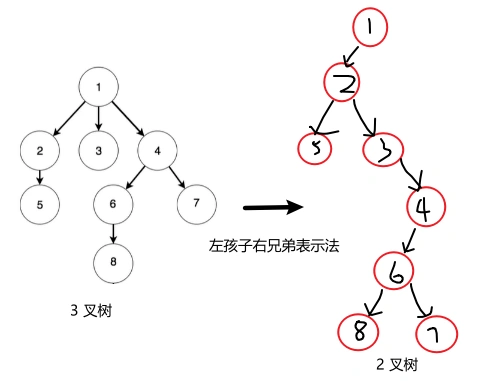
2.3 特点
- 每个节点的度最多为2;
- 度为0的节点比度为2的节点多1个;
- 证明:参考公式 —> 节点的数量等于边数加一
- xi:表示度为i的节点数,其中i 为 0,1,2。总共的节点数 = x2 + x1 + x0,度为2提供的边数:2x2, 度为1提供的边数:x1,度为0提供的边数:0;所以 节点数 = 边数 + 1==> x2 + x1 + x0 = 2x2 + x1 + 1 ==> x0 = x2 + 1
2.4 遍历
- 二叉树的遍历是指从二叉树的根结点出发,按照某种次序依次访问二叉树中的所有结点,使得每个结点仅被访问一次。
- 二叉树的访问次序:前序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历
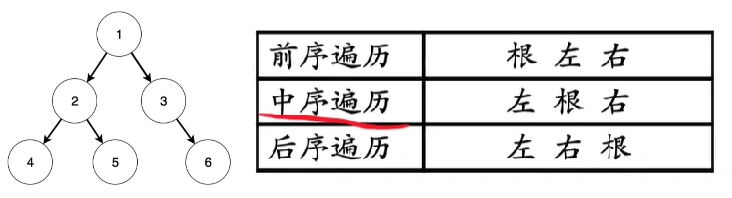
- 前序遍历:1→2→4→5→3→6
- 中序遍历:4→2→5→1→3→6
- 后序遍历:4→5→2→6→3→1
2.5 分类
- 中国版

- 国际版
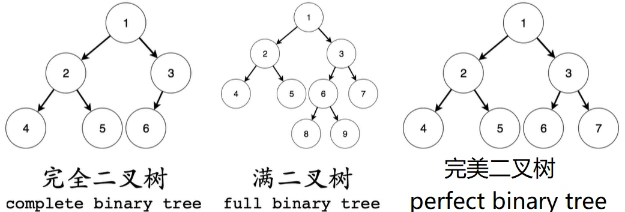
- 完美二叉树:叶子节点都在同一层并且除叶子节点外的所有节点都有两个子节点;
- 完全二叉树(重点):对于一颗二叉树,假设其深度为d(d>1)。除第d层外的所有节点构成完美二叉树,且第d层所有节点从左向右连续地紧密排列,这样的二叉树被称为完全二叉树;
- 完全二叉树的优势:从根节点到叶子节点中的每一个节点进行一个顺序(连续)标号;
- 完全二叉树的特点:
- 编号为i的子节点:左孩子编号为2i,右孩子编号为2i+1,注:i ≥ 1;
- 若 i 从0 开始标记,则左孩子编号为2i + 1,右孩子编号为2i+2,无意中多了一次加法运算;(不建议)
- 可以用连续空间存储(数组);
- 完全二叉树实现方式:顺序表 和 链表
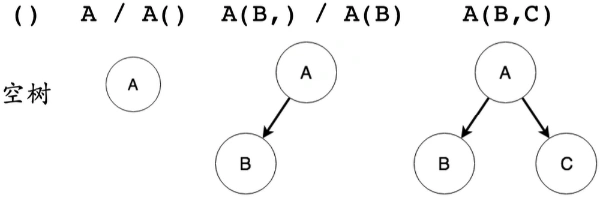
2.6 广义表
可以使用广义表来表示一颗二叉树
2.7 二叉排序树
- 本质:基于二叉树这种结构,定义了一种性质,并且在不断维护这种性质的一种新结构。
- 性质:一颗二叉树中的任何三元组都满足 B(左孩子) < A(根节点) < C (右孩子)的这种关系。故中序遍历即可实现排序操作。
- 补充:数据结构的本质:定义一种性质,并且维护这种性质的一种结构
2.8 广义表转二叉树
- 通过“栈”这种数据结构实现广义表转二叉树;
3 代码展示
3.1 二叉排序树
#include
#include
#include
typedef struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *lchild, *rchild;
} Node;
typedef struct Tree {
Node *root;
int length; // 记录二叉树的节点个数
} Tree;
Node *getNewNode(int val);
Tree *getNewTree();
Node *insert\_node(Node *, int, int *);
void insert(Tree *, int);
void pre\_order\_node(Node *);
void pre\_order(Tree *);
void in\_order\_node(Node *);
void in\_order(Tree *);
void post\_order\_node(Node *);
void post\_order(Tree *);
void clear\_node(Node *);
void clear(Tree *);
void output\_node(Node *);
void output(Tree *);
int main() {
srand(time(0));
Tree *tree = getNewTree();
#define MAX\_OP 10
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_OP; i++) {
int val = rand() % 100;
insert(tree, val);
output(tree);
}
#undef MAX\_OP
pre_order(tree);
in_order(tree);
post_order(tree);
clear(tree);
return 0;
}
Node *getNewNode(int val) {
Node *p = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
p->data = val;
p->lchild = p->rchild = NULL;
return p;
}
Tree *getNewTree() {
Tree *t = (Tree *)malloc(sizeof(Tree));
t->root = NULL;
t->length = 0;
return t;
}
// ⼆叉排序树插入操作
// 性质:一颗二叉树中的任何三元组都满足 B(左孩子) < A(根节点) < C (右孩子)的这种关系,故中序遍历可实现排序
// 插入过程(尾插法):从根节点开始,找到待插入位置前的叶子节点(向下寻找),然后返回各个节点地址(向上回溯)
Node *insert\_node(Node *root, int val, int *flag) {
if (root == NULL) {
*flag = 1;
return getNewNode(val);
}
if (root->data == val) return root; // ⼆叉排序树的性质:任何三元组都满足 B(左孩子) < A(根节点) < C (右孩子)
if (root->data > val) root->lchild = insert_node(root->lchild, val, flag);
else root->rchild = insert_node(root->rchild, val, flag);
return root;
}
void insert(Tree *t, int val) {
if (t == NULL) return ;
int flag = 0; // 传出参数,标记当前插入节点是否成功,成功:1,失败:0
t->root = insert_node(t->root, val, &flag);
t->length += flag;
return ;
}
// 前序:根->左->右
void pre\_order\_node(Node *root) {
if (root == NULL) return ;
printf("%d ", root->data);
pre_order_node(root->lchild);
pre_order_node(root->rchild);
return ;
}
void pre\_order(Tree *t) {
if (t == NULL) return ;
printf("pre\_order : ");
pre_order_node(t->root);
printf("\n");
return ;
}
// 中序:左->根->右
void in\_order\_node(Node *root) {
if (root == NULL) return ;
in_order_node(root->lchild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
in_order_node(root->rchild);
return ;
}
void in\_order(Tree *t) {
if (t == NULL) return ;
printf("in\_order : ");
in_order_node(t->root);
printf("\n");
return ;
}
// 后序:左->右->根
void post\_order\_node(Node *root) {
if (root == NULL) return ;
post_order_node(root->lchild);
post_order_node(root->rchild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
return ;
}
void post\_order(Tree *t) {
if (t == NULL) return ;
printf("post\_order : ");
post_order_node(t->root);
printf("\n");
return ;
}
// 从叶子节点开始删除
void clear\_node(Node *node) {
if (node == NULL) return ;
clear_node(node->lchild);
clear_node(node->rchild);
free(node);
return ;
}
void clear(Tree *t) {
if (t == NULL) return ;
clear_node(t->root);
}
// 相当于前序遍历
void output\_node(Node *root) {
if (root == NULL) return ;
printf("%d", root->data);
if (root->lchild == NULL && root->rchild == NULL) return ; // 若是叶子节点,则结束
printf("(");
output_node(root->lchild);
printf(",");
output_node(root->rchild);
printf(")");
return ;
}
void output(Tree *t) {
if (t == NULL) return ;
printf("tree(%d) : ", t->length);
output_node(t->root);
printf("\n");
}
// tree(1) : 6
// tree(2) : 6(,28)
// tree(3) : 6(,28(9,))
// tree(4) : 6(,28(9,87))
// tree(5) : 6(,28(9,87(61,)))
// tree(6) : 6(,28(9,87(61(34,),)))
// tree(7) : 6(,28(9,87(61(34(,40),),)))
// tree(8) : 6(,28(9,87(61(34(,40),65),)))
// tree(9) : 6(,28(9(,20),87(61(34(,40),65),)))
// tree(9) : 6(,28(9(,20),87(61(34(,40),65),)))
// pre\_order : 6 28 9 20 87 61 34 40 65
// in\_order : 6 9 20 28 34 40 61 65 87
// post\_order : 20 9 40 34 65 61 87 28 6
3.2 广义表转二叉树
#include
#include
#include
//⼆叉树的结构定义
typedef struct Node {
char data;
struct Node *lchild, *rchild;
} Node;
typedef struct Tree {
Node *root;
int length;
} Tree;
//栈的结构定义(存储⼆叉树节点地址)
typedef struct Stack {
Node **data; // 定义二级指针的原因:使用数组来存放每个节点的地址,即数组的每个元素都是 Node*
int top, size; // top: 标记栈顶位置,默认为-1;size: 当前栈空间的大小
} Stack;
Node *getNewNode(char); // 节点的初始化
Tree *getNewTree(); // ⼆叉树的初始化
void clear\_node(Node *); // 销毁⼆叉树的节点
void clear\_tree(Tree *); // 销毁⼆叉树
Stack *init\_stack(int); // 栈的初始化
void clear\_stack(Stack *); // 栈的销毁
Node *top(Stack *); // 输出栈顶元素
int empty(Stack *); // 栈的判空
int push(Stack *, Node *); // 压栈操作
int pop(Stack *); // 弹栈操作
void pre\_order\_node(Node *);
void pre\_order(Tree *); // 前序遍历
void in\_order\_node(Node *);
void in\_order(Tree *); // 中序遍历
void post\_order\_node(Node *);
void post\_order(Tree *); // 后序遍历
Node *build(const char *, int *); // 构建一颗二叉树
int main() {
char str[1000] = { 0 };
int node_num = 0;
scanf("%[^\n]s", str);
getchar();
Tree *tree = getNewTree();
tree->root = build(str, &node_num);
tree->length = node_num;
pre_order(tree);
in_order(tree);
post_order(tree);
clear_tree(tree);
return 0;
}
Node *getNewNode(char val) {
Node *p = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
p->lchild = p->rchild = NULL;
p->data = val;
return p;
}
Tree *getNewTree() {
Tree *t = (Tree *)malloc(sizeof(Tree));
t->root = NULL;
t->length = 0;
return t;
}
void clear\_node(Node *root) {
if (root == NULL) return;
clear_node(root->lchild);
clear_node(root->rchild);
free(root);
return;
}
void clear\_tree(Tree *t) {
if (t == NULL) return;
clear_node(t->root);
free(t);
return;
}
Stack *init\_stack(int n) {
Stack *s = (Stack *)malloc(sizeof(Stack));
s->data = (Node **)malloc(sizeof(Node *) * n);
s->top = -1;
s->size = n;
return s;
}
void clear\_stack(Stack *s) {
if (s == NULL) return;
free(s->data);
free(s);
return;
}
Node *top(Stack *s) {
return s->data[s->top];
}
int empty(Stack *s) {
return s->top == -1;
}
int push(Stack *s, Node *val) {
if (s == NULL) return 0;
if (s->top == s->size - 1) return 0;
s->data[++(s->top)] = val;
return 1;
}
int pop(Stack *s) {
if (s == NULL) return 0;
if (empty(s)) return 0;
s->top -= 1;
return 1;
}
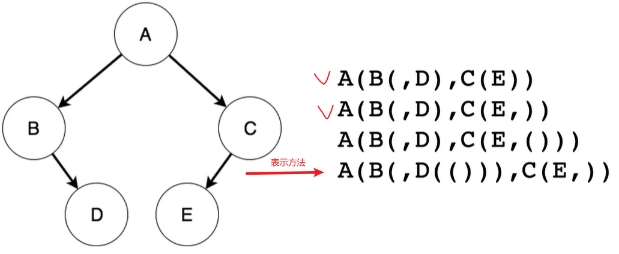
// 二叉树的广义表表示:str = "A(B(, D), C(E))"
// '(': 根节点入栈,设置flag=0; ')': 出栈; ',': 设置flag=1;
// flag=0: 表示是左子节点, flag=1: 表示是右子节点
// 将广义表转化为二叉树
// 前序|后续遍历 && 中序遍历 ==> 二叉树
// 本方法:栈实现广义表转二叉树
// 方法2:系统栈(递归)实现广义表转二叉树
Node *build(const char *str, int *node\_num) {
Stack *s = init_stack(strlen(str));
int flag = 0;
Node *temp = NULL, *p = NULL; // temp:指向每层的父节点,p:指向根节点
while (str[0]) {
switch (str[0]) {
case '(':
push(s, temp);
flag = 0;
break;
case ')':
p = top(s);
pop(s);
break;
case ',': flag = 1; break;
case ' ': break;
default:
temp = getNewNode(str[0]);
if (!empty(s) && flag == 0) {
top(s)->lchild = temp;
}
else if (!empty(s) && flag == 1) {
top(s)->rchild = temp;
}
++(*node_num);
break;
}
++str;
}
clear_stack(s);
if (temp && p == NULL) p = temp; // 只有根节点的情况
return p;
}
void in\_order\_node(Node *root) {
if (root == NULL) return;
in_order_node(root->lchild);
printf("%c ", root->data);
in_order_node(root->rchild);
return;
}
void in\_order(Tree *tree) {
if (tree == NULL) return;
printf("in\_order(%d) : ", tree->length);
in_order_node(tree->root);
printf("\n");
return;
}
void pre\_order\_node(Node *root) {
if (root == NULL) return;
printf("%c ", root->data);
pre_order_node(root->lchild);
pre_order_node(root->rchild);
return;
}
void pre\_order(Tree *tree) {
if (tree == NULL) return;
printf("pre\_order(%d) : ", tree->length);
pre_order_node(tree->root);
printf("\n");
return;
}
void post\_order\_node(Node *root) {
if (root == NULL) return;
post_order_node(root->lchild);
post_order_node(root->rchild);
printf("%c ", root->data);
return;
}
void post\_order(Tree *tree) {
if (tree == NULL) return;
printf("post\_order(%d) : ", tree->length);
post_order_node(tree->root);
printf("\n");
return;
}
转载请注明:xuhss » 二叉树的创建、遍历、广义表转换