Python微信订餐小程序课程视频
https://edu.csdn.net/course/detail/36074
Python实战量化交易理财系统
https://edu.csdn.net/course/detail/35475
本文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/snoopy1866/p/16069000.html
定性检测的样本量估算常用单组目标值法和抽样误差法,《体外诊断试剂临床试验技术指导原则》(2017年第72号)中提到:当评价指标P接近100%时,这两种样本量估算方法可能不适用,应考虑更加适宜的方法进行样本量估算和统计学分析,如精确概率法。
1. PASS软件估计样本量
PASS 软件提供的 Test for One Proportion 模块提供了精确概率法的选项,在 Power Calculation Method 中选择 Binomial Enumeration 即可。SAS 软件的 PROC POWER 过程则不支持精确概率法。
例如:某试剂的阳性符合率预期值为98%,目标值为95%,取显著性水平α=0.05,检验效能1-β=0.8,试估计所需样本量。
由于98%接近100%,因此采用精确概率法计算样本量。在 PASS 软件中设置相关参数,计算所需样本量为312。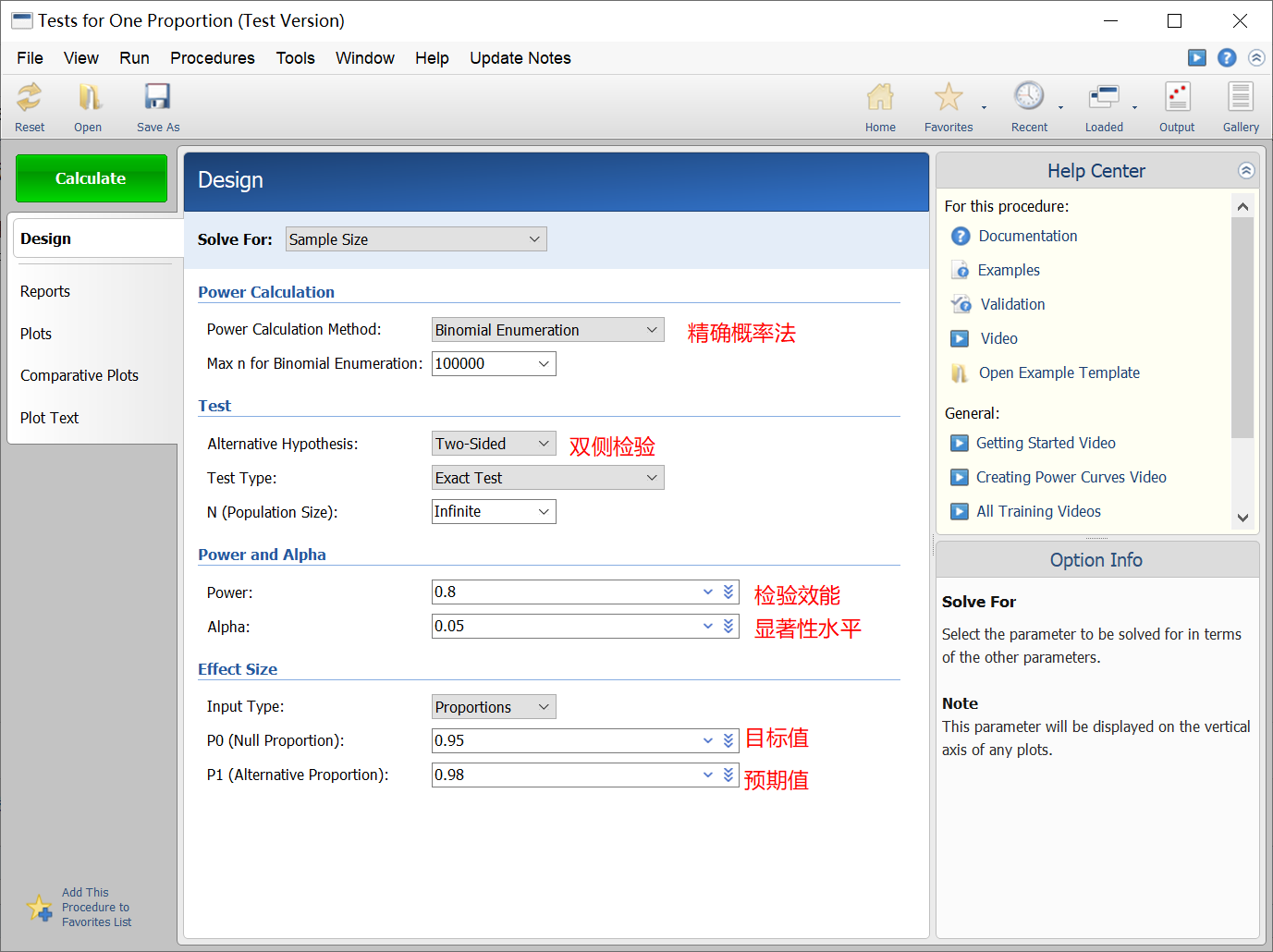
2. 功效曲线的"锯齿状"现象
需要注意的是:PASS软件通过迭代寻找满足检验效能高于0.8的样本量,当找到一个满足条件的样本量时,PASS即中止迭代,然而此时的样本量有可能并不是保守的。下面将展示这种“不保守”的现象。
在PASS软件中,我们设定求解目标为Power,样本量取值为区间[310, 370],绘制功效曲线如下: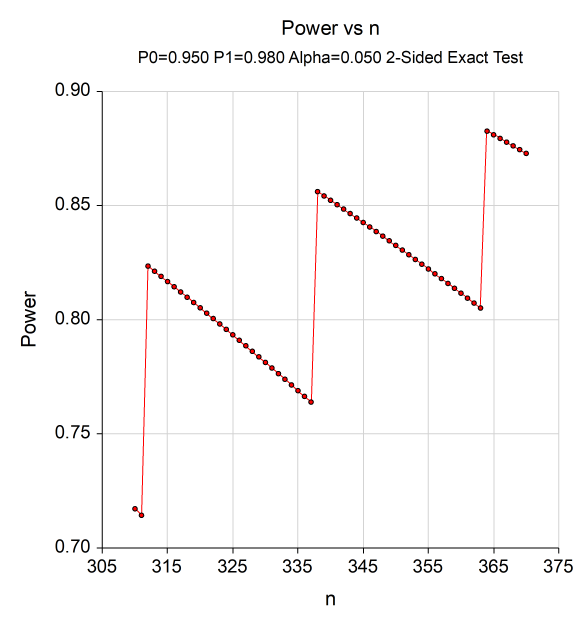
可以发现:检验效能并非随着样本量增加而单调增加,而是显示出“锯齿状”(saw-toothed),即使样本量高于PASS软件计算出的312,也存在检验效能低于0.8的情况,当且仅当样本量≥338时,才能保证检验效能稳定在0.8以上。造成此现象的原因是二项分布的离散性。
3. SAS 宏程序
以下SAS宏代码可用于计算给定参数下的精确概率法的最保守样本量,供参考。
程序的基本思路如下:
Step1. 使用 PROC POWER 过程的近似正态法计算一个粗略的样本量 n1
Step2. 在 n1 附近找一个区间,区间上下界通过参数 lbound_rate 和 ubound_rate 控制
Step3. 使用 PROC POWER 过程计算样本量在区间 [lbound_rate n1, ubound_rate n1] 的检验效能
Step4. 判断区间 [lbound_rate n1, ubound_rate n1] 内是否存在满足任意 n>n0,使得 power(n) > 0.8 且 n0 之后的第一个波谷满足 power > 0.8 的 n0
Step5. 如 Step 4 找到了满足条件的n0,则输出样本量计算结果;否则,根据参数 expand_step 扩展区间上界,重复 Step1-Step4
/*
宏程序功能:单组目标值-精确概率法,计算最保守样本量,计算结果未考虑脱落率。
*/
%macro SampleSize_ExactBinomial(p0, p1, alpha = 0.05, power = 0.8, lbound_rate = 0.8, ubound_rate = 1.2, expand_step = 2
OutDataSet = SampleSize_ExactBinomial, DetailInfo = DetainInfo,
PowerPlot = Y);
/*
--------------宏参数-----------------
p0: 目标值
p1: 预期值
alpha: 显著性水平
power: 检验效能
lbound\_rate: 寻值区间下界比例
ubound\_rate: 寻值区间上界比例
expand\_step: 扩展区间步长
OutDataSet: 输出样本量估算结果的数据集名称
DetailInfo: 输出样本量估算细节的数据集名称
PowerPlot: 是否绘制功效图
----------------宏变量---------------
ntotal\_normal: 正态近似法估算的样本量
ntotal\_lbound: 寻值区间下界
ntotal\_ubound: 寻值区间上界
IsLocalFindFirst: 是否找到首次满足检验效能的不保守样本量
IsGlobalFind: 是否找到稳定满足检验效能的最保守样本量
LooseMinSampleSize: 首次满足检验效能的不保守样本量
StrictMinSampleSize:稳定满足检验效能的最保守样本量
ActualPower: 最保守样本量下的实际检验效能
*/
/*近似正态法求得一个粗略的样本量*/
ods output output = output_normal;
proc power;
onesamplefreq test = z method = normal
alpha = &alpha
power = &power
nullproportion = &p0
proportion = &p1
ntotal = .;
run;
proc sql noprint;
select ntotal into: ntotal_normal from output_normal; /*提取正态近似样本量*/
quit;
%let ntotal_lbound = %sysfunc(floor(%sysevalf(&lbound_rate*&ntotal_normal))); /*寻值区间下界*/
%let ntotal_ubound = %sysfunc(ceil(%sysevalf(&ubound_rate*&ntotal_normal))); /*寻值区间上界*/
/*在区间[&ntotal\_lbound, &ntotal\_ubound]内多次求Power*/
ods output output = output_exact;
proc power;
onesamplefreq test = exact
alpha = &alpha
power = .
nullproportion = &p0
proportion = &p1
ntotal = &ntotal_lbound to &ntotal_ubound by 1;
%if &PowerPlot = Y %then %do;
plot x = n min = &ntotal_lbound max = &ntotal_ubound step = 1
yopts = (ref = &power) xopts = (ref = &ntotal_normal);
%end;
run;
/*左邻点*/
data power_exact_left;
if _n_ = 1 then do;
ntotal = &ntotal_lbound;
power_left = .;
output;
end;
set output_exact(rename = (power = power_left)
keep = ntotal power
firstobs = 1 obs = %eval(&ntotal_ubound - &ntotal_lbound));
ntotal = ntotal + 1;
label power_left = "左邻点";
output;
run;
/*目标点*/
data power_exact_mid;
set output_exact(rename = (power = power_mid) keep = ntotal power);
label power_mid = "目标点";
run;
/*右邻点*/
data power_exact_right;
set output_exact(rename = (power = power_right)
keep = ntotal power
firstobs = 2 obs = %eval(&ntotal_ubound - &ntotal_lbound + 1));
ntotal = ntotal - 1;
label power_right = "右邻点";
output;
if _n_ = %eval(&ntotal_ubound - &ntotal_lbound) then do;
ntotal = &ntotal_ubound;
power_right = .;
output;
end;
run;
/*寻找最保守的样本量*/
%let IsLocalFindFirst = 0;
%let IsGlobalFind = 0;
data &DetailInfo;
merge power_exact_left
power_exact_mid
power_exact_right;
label ntotal = "当前样本量"
power_left = "左侧点效能"
power_mid = "当前点效能"
power_right = "右侧点效能"
min_sample_size = "已知最低样本量"
is_local_find_first = "首次局部最优解"
is_local_find = "局部最优解"
is_global_find = "全局最优解"
peak = "波峰"
trough = "波谷";
retain min_sample_size 0
is_local_find 0
is_local_find_first 0
is_global_find 0;
if ntotal > &ntotal_lbound and ntotal < &ntotal_ubound then do;
if power_left < power_mid and power_right < power_mid then peak = "Yes";
if power_left > power_mid and power_right > power_mid then trough = "Yes";
if power_mid > &power and is_local_find = 0 then do; /*局部最优解,标记到达检验效能的样本量*/
min_sample_size = ntotal;
is_local_find = 1;
if is_local_find_first = 0 then do; /*首次达到局部最优解,可视为不保守的样本量估算结果*/
is_local_find_first = 1;
call symput("LooseMinSampleSize", min_sample_size);
call symput("IsLocalFindFirst", is_local_find_first);
end;
end;
if power_mid < &power and is_local_find = 1 then do; /*局部最优解的破坏,锯齿状的波谷导致此时的检验效能无法稳定在所需大小之上*/
min_sample_size = .;
is_local_find = 0;
end;
if power_mid > &power and is_local_find = 1 and is_global_find = 0 and trough = "Yes" then do; /*全局最优解,此时即便是波谷也能达到所需的检验效能,可视为最保守的样本量估算结果*/
is_global_find = 1;
call symput("StrictMinSampleSize", min_sample_size);
call symput("ActualPower", power_mid);
call symput("IsGlobalFind", is_global_find);
end;
end;
run;
%if &IsLocalFindFirst = 1 and &IsGlobalFind = 1 %then %do; /*当前区间内找到最保守的样本量,输出结果*/
/*输出样本量估算结果*/
data &OutDataSet;
length Exact1 $50 Exact2 $50;
label P0 = "目标值"
P1 = "预期值"
ALPHA = "显著性水平"
POWER = "检验效能"
Normal = "正态近似"
Exact1 = "精确概率法(不保守)"
Exact2 = "精确概率法(最保守)";
P0 = &p0;
P1 = &p1;
ALPHA = α
POWER = &power;
Normal = &ntotal_normal;
%if &IsLocalFindFirst = 1 %then %do; Exact1 = put(&LooseMinSampleSize, best.); %end;
%else %do; Exact1 = "Outside the interval [&ntotal\_lbound, &ntotal\_ubound]"; %end;
%if &IsGlobalFind = 1 %then %do; Exact2 = put(&StrictMinSampleSize, best.); %end;
%else %do; Exact2 = "Outside the interval [&ntotal\_lbound, &ntotal\_ubound]"; %end;
run;
/*删除数据集*/
proc delete data = output_exact
output_normal
power_exact_left
power_exact_mid
power_exact_right;
run;
/*输出日志*/
%put NOTE: 参数:&=p0, &=p1, &=alpha, &=power;
%put NOTE: 正态近似法求得最低样本量为&ntotal_normal;
%if &IsLocalFindFirst = 1 %then %do;
%put NOTE: 精确概率法求得首次达到检验效能的最低样本量为 %sysfunc(strip(&LooseMinSampleSize)) (不保守);
%end;
%if &IsGlobalFind = 1 %then %do;
%put NOTE: 精确概率法求得最保守的样本量为 %sysfunc(strip(&StrictMinSampleSize)),实际检验效能为 &ActualPower.;
%end;
%else %do;
%put ERROR: 在样本量区间[&ntotal_lbound, &ntotal_ubound]内没有找到精确的样本量!使用参数LBOUND_RATE、UBOUND_RATE调节区间大小;
%end;
%end;
%else %do; /*当前区间内未找到最保守的样本量,扩大区间继续寻找*/
%SampleSize_ExactBinomial(p0 = &p0, p1 = &p1, alpha = &alpha, power = &power, lbound_rate = &lbound_rate, ubound_rate = %sysevalf(&ubound_rate + &expand_step),
OutDataSet = &OutDataSet, DetailInfo = &DetailInfo, PowerPlot = &PowerPlot);
%end;
%mend;
/*Examples
%SampleSize\_ExactBinomial(p0 = 0.94, p1 = 0.98);
%SampleSize\_ExactBinomial(p0 = 0.94, p1 = 0.98, alpha = 0.1);
%SampleSize\_ExactBinomial(p0 = 0.94, p1 = 0.98, alpha = 0.1, power = 0.9);
%SampleSize\_ExactBinomial(p0 = 0.94, p1 = 0.98, alpha = 0.1, power = 0.9, lbound\_rate = 0.8, ubound\_rate = 1.3);
%SampleSize\_ExactBinomial(p0 = 0.94, p1 = 0.98, OutDataSet = SS);
%SampleSize\_ExactBinomial(p0 = 0.94, p1 = 0.98, OutDataSet = SS, DetailInfo = Info);
%SampleSize\_ExactBinomial(p0 = 0.94, p1 = 0.98, OutDataSet = SS, DetailInfo = Info, PowerPlot = N);
data param;
n = 1;
do p1 = 0.940 to 0.980 by 0.002;
call execute('%nrstr(%SampleSize\_ExactBinomial(p0 = 0.90, p1 = '||p1||', lbound\_rate = 0.6, ubound\_rate = 1.2, OutDataSet = SS'||strip(put(n, best.))||', PowerPlot = N))');
n = n + 1;
output;
end;
run;
data SS;
set SS1-SS21;
run;
*/
参考文献:
- Vezzoli S, CROS NT V. Evaluation of Diagnostic Agents: a SAS Macro for Sample Size Estimation Using Exact Methods[C]//SAS Conference Proceedings: Pharmaceutical Users Software Exchange. 2008: 12-15.
- Chernick M R, Liu C Y. The saw-toothed behavior of power versus sample size and software solutions: single binomial proportion using exact methods[J]. The American Statistician, 2002, 56(2): 149-155.
- AKTAŞ ALTUNAY S. Effect Size For Saw Tooth Power Function in Binomial Trials[J]. 2015.
转载请注明:xuhss » 定性检测的样本量估算之精确概率法