Python微信订餐小程序课程视频
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_56069948/article/details/122285951
Python实战量化交易理财系统
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_56069948/article/details/122285941
一、约定编程
Spring AOP是一种约定流程的编程,咱们可以先通过动态代理模式的实现来理解Spring AOP的概念。
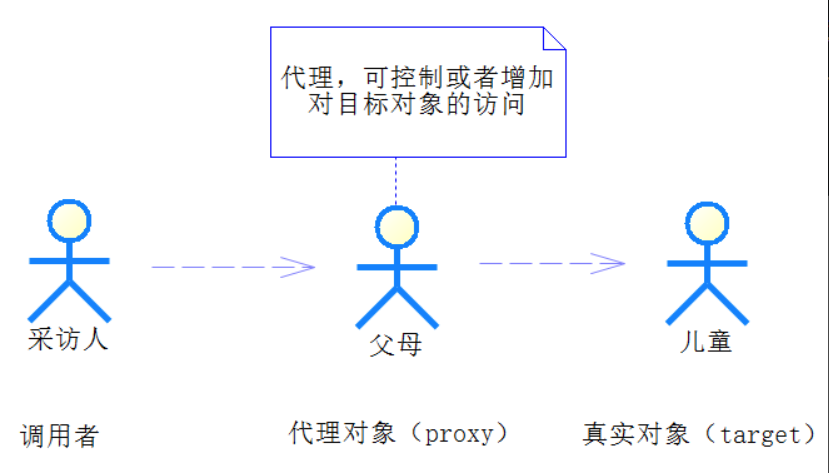
代理的逻辑很简单,例如,当你需要采访一名儿童时,首先需要经过他父母的同意,在一些问题上父母也许会替他回答,而对于另一些问题,也许父母觉得不太适合这个小孩会拒绝掉,显然这时父母就是这名儿童的代理(proxy)了。通过代理可以增强或者控制对儿童这个真实对象(target)的访问。
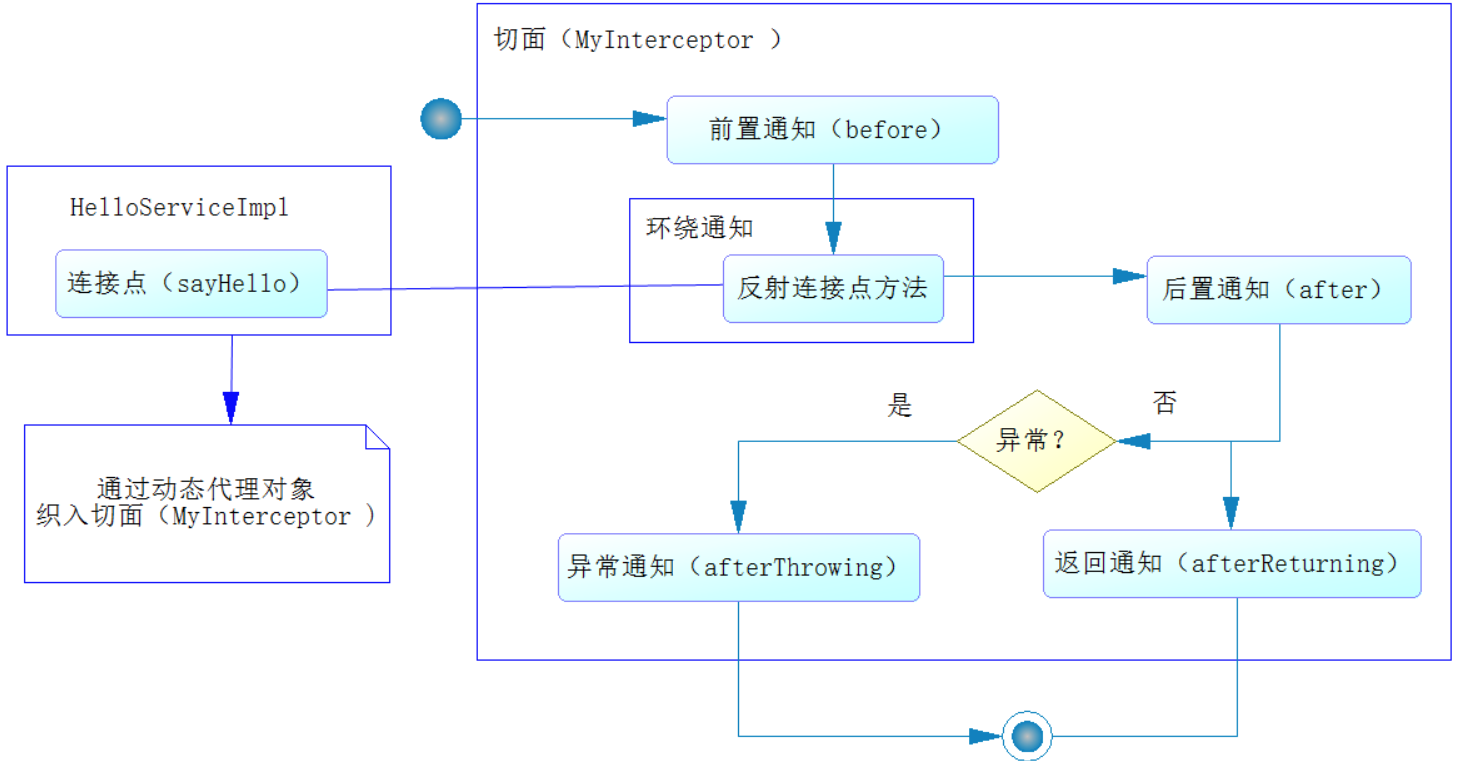
- 首先实现拦截器接口Interceptor(自己定义的接口)
下面代码均使用spring boot 2.6.2
package com.springboot.chapter4.intercept;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import com.springboot.chapter4.invoke.Invocation;
public class MyInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public boolean before() {
System.out.println("before ......");
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean useAround() {
return true;
}
@Override
public void after() {
System.out.println("after ......");
}
@Override
public Object around(Invocation invocation)
throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException
{
System.out.println("around before ......");
Object obj = invocation.proceed();
System.out.println("around after ......");
return obj;
}
@Override
public void afterReturning() {
System.out.println("afterReturning......");
}
@Override
public void afterThrowing() {
System.out.println("afterThrowing......");
}
}
2 创建代理对象
在Java的JDK中,提供了类Proxy的静态方法——newProxyInstance,给予我们来生成一个代理对象(proxy):
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader classLoader, Class[] interfaces,
InvocationHandler invocationHandler) throws IllegalArgumentException它有3个参数:
•classLoader——类加载器;(被代理的类)
•interfaces——绑定的接口,也就是把代理对象绑定到哪些接口下,可以是多个;(被代理的类实现的接口列表)
•invocationHandler ——绑定代理对象逻辑实现。
这里的invocationHandler是一个接口InvocationHandler对象,它定义了一个invoke方法,这个方法就是实现代理对象的约定流程
package com.springboot.chapter4.proxy;
package com.springboot.chapter4.proxy;
/**** imports ****/
public class ProxyBean implements InvocationHandler {
private Object target = null;//代理对象
private Interceptor interceptor = null;//拦截器
public ProxyBean (Object target,Interceptor interceptor){
this.target=target;
this.interceptor=interceptor;
}
/**
* 处理代理对象方法逻辑
* @param proxy 代理对象
* @param method 当前方法
* @param args 运行参数
* @return 方法调用结果
* @throws Throwable 异常
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) {
// 异常标识
boolean exceptionFlag = false;
Invocation invocation = new Invocation(target, method, args);
Object retObj = null;
try {
if (this.interceptor.before()) {
retObj = this.interceptor.around(invocation);
} else {
retObj = method.invoke(target, args);
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
// 产生异常
exceptionFlag = true;
}
this.interceptor.after();
if (exceptionFlag) {
this.interceptor.afterThrowing();
} else {
this.interceptor.afterReturning();
return retObj;
}
return null;
}
}从上面例子可以看到:代理对象proxyBean定义了织入流程即invoke方法,将拦截器MyInterceptor包装到目标对象tagert的method上。
- 测试效果
/**
* 绑定代理对象
* @param target 被代理对象
* @param interceptor 拦截器
* @return 代理对象
*/
public static Object getProxyObject(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) {
ProxyBean proxyBean = new ProxyBean(target,interceptor);//proxyBean定义了织入流程即invoke方法
// 生成代理对象
Object proxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance( target.getClass().getClassLoader(),
target.getClass().getInterfaces(),
proxyBean);//proxyBean实现target对象的接口列表,实现方式为调用代理对象的方法时通过invoke(invoke可调用target对象的方法)调用target对象对应的方法。
// 返回代理对象
return proxy;
}private static void testProxy() {
IHelloService helloService = new HelloServiceImpl();//被代理对象
// 按约定获取proxy
IHelloService proxy = (IHelloService) getProxyObject(
helloService, new MyInterceptor());
proxy.sayHello("zhangsan");
System.out.println("\n###############name is null!!#############\n");
proxy.sayHello(null);
}二、Spring AOP概念和术语
Spring AOP是一种基于方法的AOP,它只能应用于方法上。在Spring中可以使用多种方式配置AOP,因为Spring Boot采用注解方式,所以这里只介绍使用@AspectJ注解的方式。AOP可以减少大量重复的工作,最为典型的应用场景就是数据库事务的管控。比如数据库的打开和关闭以及事务的提交和回滚都有流程默认给你实现。换句话说,你都不需要完成它们,你需要完成的任务是编写SQL这一步而已,然后织入流程中。

@Autowired
private UserDao = null;
......
@Transactional
public int inserUser(User user) {
return userDao.insertUser(user);
}这里可以看到仅仅使用了一个注解@Transactional,表明该方法需要事务运行,没有任何数据库打开和关闭的代码,也没有事务回滚和提交的代码,却实现了数据库资源的打开和关闭、事务的回滚和提交。
1.AOP术语:
•连接点(join point):对应的是具体被拦截的对象,因为Spring只能支持方法,所以被拦截的对象往往就是指特定的方法,例如,我们前面提到的HelloServiceImpl的sayHello方法就是一个连接点,AOP将通过动态代理技术把它织入对应的流程中。
•切点(point cut):有时候,我们的切面不单单应用于单个方法,也可能是多个类的不同方法,这时,可以通过正则式和指示器的规则去定义,从而适配连接点。切点就是提供这样一个功能的概念。
•通知(advice):就是按照约定的流程下的方法,分为前置通知(beforeadvice)、后置通知(after advice)、环绕通知(around advice)、事后返回通知(afterReturning advice)和异常通知(afterThrowing advice),它会根据约定织入流程中,需要弄明白它们在流程中的顺序和运行的条件。
•目标对象(target):即被代理对象,例如,约定编程中的HelloServiceImpl实例就是一个目标对象,它被代理了。
•引入(introduction):是指引入新的类和其方法,增强现有Bean的功能。
•织入(weaving):它是一个通过动态代理技术,为原有服务对象生成代理对象,然后将与切点定义匹配的连接点拦截,并按约定将各类通知织入约定流程的过程。
•切面(aspect):是一个可以定义切点、各类通知和引入的内容,Spring AOP将通过它的信息来增强Bean的功能或者将对应的方法织入流程。
2.具体实现
2.1.添加maven依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aopartifactId>
dependency>2.2. 定义切面
首先Spring是以@Aspect作为切面声明的,当以@Aspect作为注解时,Spring就会知道这是一个切面,然后我们就可以通过各类注解(@Before、@After、@AfterReturning和@AfterThrowing)来定义各类的通知了。
package com.springboot.chapter4.aspect;
/**** imports ****/@Component //注入到Spring IOC
@Aspect //定义切面
public class MyAspect {
//引入
@DeclareParents(value= "co.springboot.chapter4.aspect.service.impl.UserServiceImpl",defaultImpl=UserValidatorImpl.class)
public UserValidator userValidator;
//定义切点
@Pointcut("execution(* com.springboot.chapter4.aspect.service.impl.UserServiceImpl.printUser(..))")
public void pointCut() {
}
//无参模式
@Before("pointCut()")
public void before() {
System.out.println("before ......");
}
//获取参数模式
//方式1:切点处加入对应的正则式
//方式2:对于非环绕通知还可以使用一个连接点(JoinPoint)类型的参数,通过它也可以获取参数
//正则式pointCut() && args(user)中,pointCut()表示启用原来定义切点的规则,并且约定将连接点(目标对象方法)名称为user的参数传递进来。这里要注意,JoinPoint类型的参数对于非环绕通知而言,Spring AOP会自动地把它传递到通知中;对于环绕通知而言,可以使用ProceedingJoinPoint类型的参数。
@Before("pointCut() && args(user)")
public void beforeParam(JoinPoint point, User user) {
Object[] args = point.getArgs();
System.out.println("before ......");
}
//环绕通知
//注意:用环绕通知注解测试的时候总是不按顺序执行,估计是Spring版本之间的差异留下的问题,这是在使用时需要注意的。所以在没有必要的时候,应尽量不要使用环绕通知,它很强大,但是也很危险。
@Around("pointCut()")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("around before......");
jp.proceed();//回调目标对象的原有方法
System.out.println("around after......");
}
@After("pointCut()")
public void after() {
System.out.println("after ......");
}
@AfterReturning("pointCut()")
public void afterReturning() {
System.out.println("afterReturning ......");
}
@AfterThrowing("pointCut()")
public void afterThrowing() {
System.out.println("afterThrowing ......");
}
}上述例子用到的基础类如下
 View Code
View Code
2.3 定义切点
execution(* com.springboot.chapter4.aspect.service.impl.UserServiceImpl.printUser(..))•execution表示在执行的时候,拦截里面的正则匹配的方法; •* 表示任意返回类型的方法;
•com.springboot.chapter4.aspect.service.impl.UserServiceImpl 指定目标对象的全限定名称;
•printUser指定目标对象的方法;
•(..)表示任意参数进行匹配。
2.4 使用@DeclareParents 定义引入
@DeclareParents,它的作用是在不侵入原有业务的前提上对原有的服务进行增强,它有两个必须配置的属性value和defaultImpl。
•value:指向你要增强功能的目标对象,这里是要增强UserServiceImpl对象,因此可以看到配置为com.springboot.chapter4.aspect.service.impl.UserServiceImpl+。
•defaultImpl:引入增强功能的类,这里配置为UserValidatorImpl,用来提供校验用户是否为空的功能。
2.5 使用切面的指示器
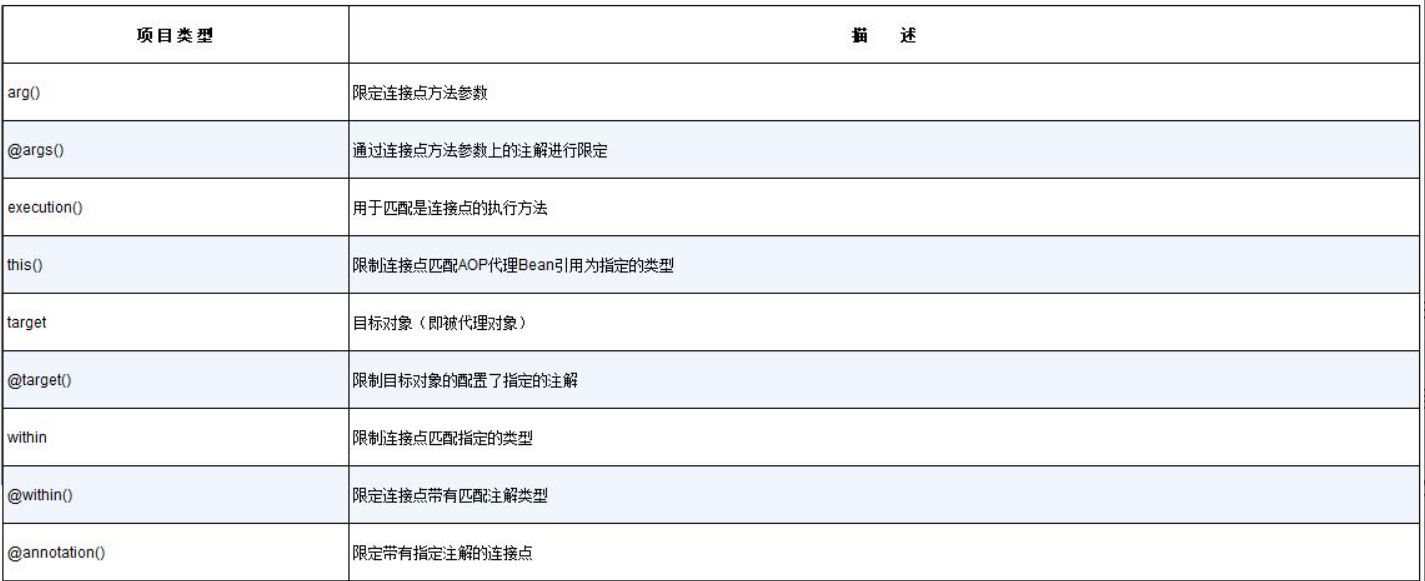
切面中可以使用的指示器如下,比如上述例子中arg()获取切点的参数值
3.测试效果
package com.springboot.chapter4.aspect.controller;
/**** imports ****/
// 定义控制器
@Controller
// 定义类请求路径
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
// 注入用户服务
@Autowired
private UserService userService = null;
// 定义请求
@RequestMapping("/print")
// 转换为JSON
@ResponseBody
public User printUser(Long id, String userName, String note) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(id);
user.setUsername(userName);
user.setNote(note);
userService.printUser(user);// 若user=null,则执行afterthrowing方法
//测试引入
UserValidator userValidator = (UserValidator)userService;
if (userValidator.validate(user)) {
userService.printUser(user);
}
return user;// 加入断点
}
}
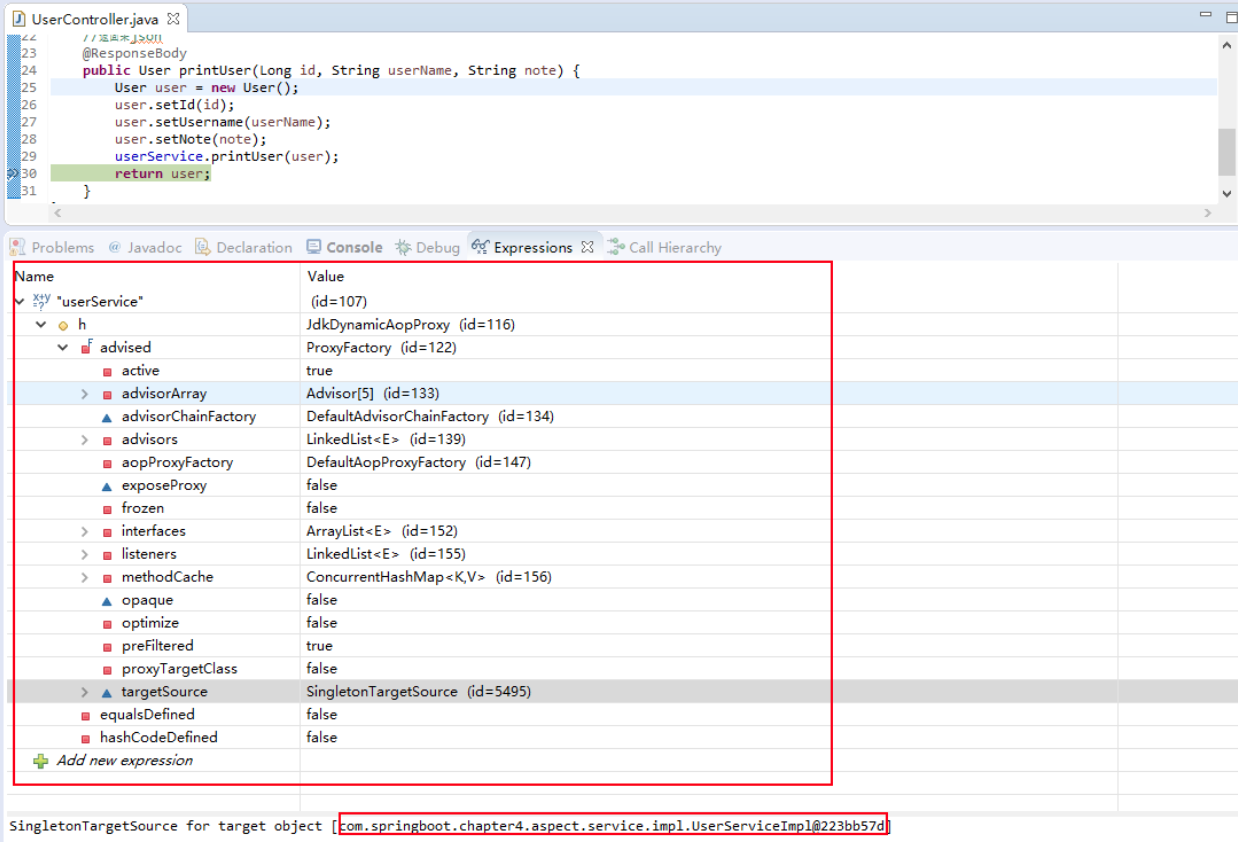
3.1未引入效果
before ......id =1 username =user_name_1 note =2323after ......afterReturning ......
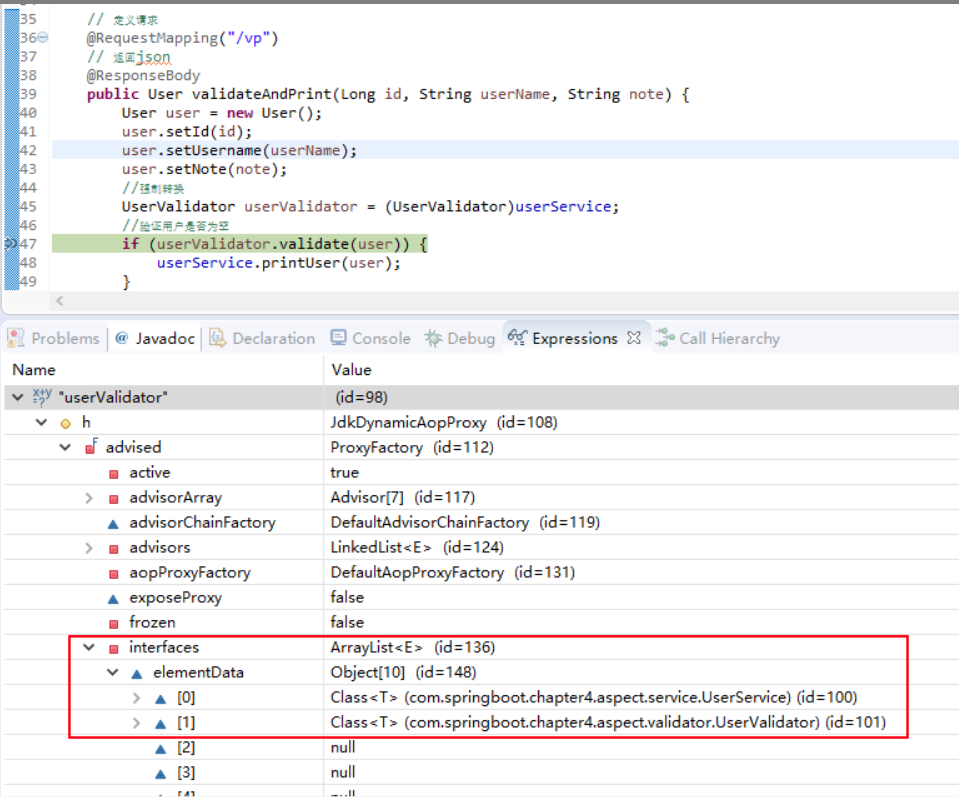
3.2引入效果
引入新的接口:UserValidatoraround before......before ......id =1 username =user_name_1 note =2323around after......after ......afterReturning ......
3.4 引入原理
这里的newProxyInstance的第二个参数为一个对象数组,也就是说这里生产代理对象时,Spring会把UserService和UserValidator两个接口传递进去,让代理对象下挂到这两个接口下,这样这个代理对象就能够相互转换并且使用它们的方法了。
Object proxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(
target.getClass().getClassLoader(),
target.getClass().getInterfaces(),
proxyBean);3.5 织入方式
上面我们都是采用接口(如UserService)+实现类(如UserServiceImpl)的模式,这是Spring推荐的方式,本书也遵循这样的方式。但是对于是否拥有接口则不是Spring AOP的强制要求,对于动态代理的也有多种实现方式,我们之前谈到的JDK只是其中的一种,业界比较流行的还有CGLIB、Javassist、ASM等。Spring采用了JDK和CGLIB,对于JDK而言,它是要求被代理的目标对象必须拥有接口,而对于CGLIB则不做要求。因此在默认的情况下,Spring会按照这样的一条规则处理,即当你需要使用AOP的类拥有接口时,它会以JDK动态代理运行,否则以CGLIB运行。
不使用接口例子
......
// 定义控制器
@Controller
// 定义类请求路径
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
// 使用非接口注入
@Autowired
private UserServiceImpl userService = null;
// 定义请求
@RequestMapping("/print")
// 返回JSON
@ResponseBody
public User printUser(Long id, String userName, String note) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(id);
user.setUsername(userName);
user.setNote(note);
userService.printUser(user);
return user;// 加入断点测试
}
......
}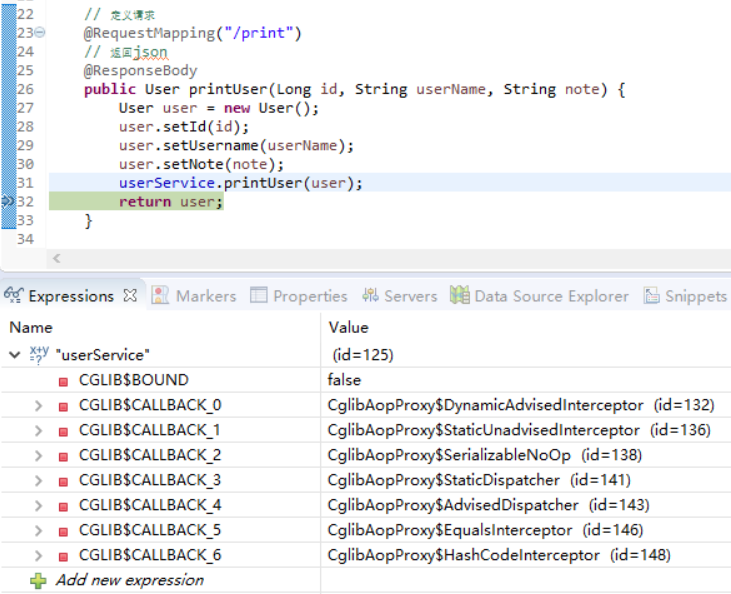
此时Spring已经使用了CGLIB为我们生成代理对象,从而将切面的内容织入对应的流程中。当使用接口时,用JDK为我们生成代理对象。
- 多个切面
Spring提供了一个注解@Order和一个接口Ordered,我们可以使用它们的任意一个指定切面的顺序。
......
@Aspect
@Order(1)
public class MyAspect1 {
......
}
//或者
......
@Aspect
public class MyAspect1 implements Ordered {
// 指定顺序
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 1;
}
....
}效果如下
MyAspect1 before ......
MyAspect2 before ......
MyAspect3 before ......
测试多个切面顺序
MyAspect3 after ......
MyAspect3 afterReturning ......
MyAspect2 after ......
MyAspect2 afterReturning ......
MyAspect1 after ......
MyAspect1 afterReturning ......转载请注明:xuhss » 约定编程与Sping AOP