Python微信订餐小程序课程视频
https://edu.csdn.net/course/detail/36074
Python实战量化交易理财系统
https://edu.csdn.net/course/detail/35475目录
正文
emptyDir临时卷
有些应用程序需要额外的存储,但并不关心数据在重启后仍然可用。
例如,缓存服务经常受限于内存大小,将不常用的数据转移到比内存慢、但对总体性能的影响很小的存储中。
再例如,有些应用程序需要以文件形式注入的只读数据,比如配置数据或密钥。
临时卷就是为此类用例设计的。因为卷会遵从 Pod 的生命周期,与 Pod 一起创建和删除, 所以停止和重新启动 Pod 时,不会受持久卷在何处可用的限制。
下面我们就通过一个临时卷,让一个pod中的两个容器实现文件共享。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: emptydirpod
namespace: chesterns
spec:
containers:
- name: writeinfo
image: centos
command: ["bash","-c","for i in {1..100};do echo $i >> /data/hello;sleep 1;done"]
volumeMounts:
- name: data
mountPath: /data
- name: readinfo
image: centos
command: ["bash","-c","tail -f /data/hello"]
volumeMounts:
- name: data
mountPath: /data
volumes:
- name: data
emptyDir: {} 验证
kubectl exec emptydirpod -c readinfo -n chesterns -- cat /data/hello回到顶部## hostPath卷
挂载Node文件系统(Pod所在节点)上文件或者目录到Pod中的容器。通常用在Pod中容器需要访问宿主机文件的场景下。
下面通过一个yaml来实现hostPath卷
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: hostpathpod
namespace: chesterns
spec:
containers:
- name: busybox
image: busybox
args:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- sleep 36000
volumeMounts:
- name: data
mountPath: /data
volumes:
- name: data
hostPath:
path: /tmp
type: Directory验证
kubectl apply -f hostpath.yaml
kubectl exec hostpathpod -n chesterns -- ls /datals /tmp回到顶部## 网络卷NFS
NFS是一个主流的文件共享服务器。可以实现分布式系统中的文件统一管理。
yum install nfs-utils -y #每个Node上都要安装nfs-utils包master上开启nfs-server
#master
vi /etc/exports
/tmp/chesternfs *(rw,fsid=0,no\_root\_squash)
mkdir -p /tmp/chesternfs
systemctl start nfs
systemctl enable nfs 定义一个deployment,使用我们刚搭建的nfssever来挂载文件
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nfsdeployment
namespace: chesterns
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
replicas: 3
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
volumeMounts:
- name: wwwroot
mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
ports:
- containerPort: 80
volumes:
- name: wwwroot
nfs:
server: 192.168.43.111
path: /tmp/chesternfs通过新建一个a.html来验证是不是挂载进了容器
vi /tmp/chesternfs/index.html/a.html
kubectl get pod -n chesterns
kubectl exec nfsdeployment-f846bc9c4-s2598 -n chesterns -- ls /usr/share/nginx/html
curl 10.244.36.122/a.html回到顶部## PV与PVC
我们可以将PV看作可用的存储资源,PVC则是对存储资源的需求,PV与PVC是为了方便我们对存储资源进行系统的管理而诞生的,有了pv和pvc我们就可以对我们所有的存储资源进行合理的分配。
pv的创建又分为静态模式与动态模式。
静态模式
集群管理员手工创建许多PV,在定义PV时需要将后端存储的特性进行设置。
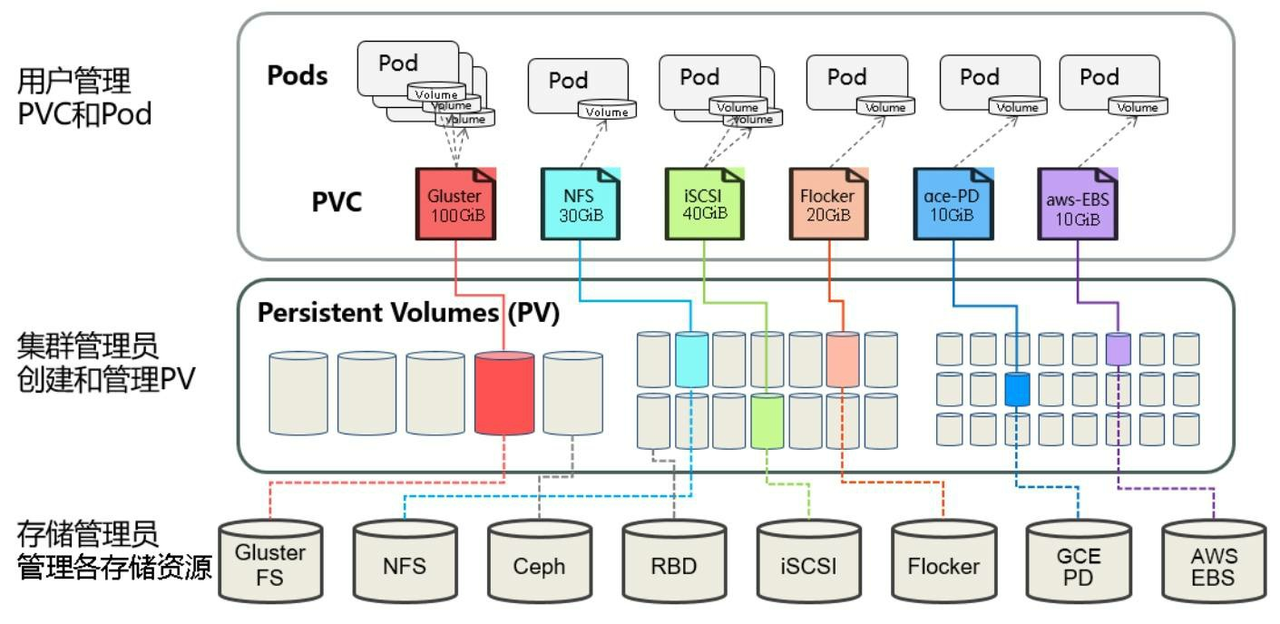
定义PV,声明需要5g空间
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: chesterpv
namespace: chesterns
spec:
capacity:
storage: 5Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
nfs:
path: /tmp/chesternfs
server: 192.168.43.111AccessModes(访问模式):
- ReadWriteOnce(RWO):读写权限,但是只能被单个节点挂载
- ReadOnlyMany(ROX):只读权限,可以被多个节点挂载
- ReadWriteMany(RWX):读写权限,可以被多个节点挂载
RECLAIM POLICY(回收策略):
通过pv的persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy字段设置
- Retain(保留):保留数据,需要管理员手工清理数据
- Recycle(回收):清除 PV 中的数据,等同执行 rm -rf /tmp/chesternfs/*
-
Delete(删除):与 PV 相连的后端存储同时删除
应用pv
kubectl apply -f pv.yamlkubectl describe pv chesterpv -n chesternsPVSTATUS(状态):
- Available(可用):表示可用状态,还未被任何 PVC 绑定
- Bound(已绑定):表示 PV 已经被 PVC 绑定
- Released(已释放):PVC 被删除,但是资源还未被集群重新声明
- Failed(失败):表示该 PV 的自动回收失败
下面我们定义pvc,设置一样的存储空间,绑定刚刚建好的pv
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: chesterpvc
namespace: chesterns
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 5Gi应用pvc
kubectl apply -f pvc.yaml
kubectl describe pvc chesterpvc -n chesterns
kubectl describe pv chesterpv -n chesterns使用PVC,我们定义一个pod,指定挂载用的pvc
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: chesterpvcpod
namespace: chesterns
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80
volumeMounts:
- name: www
mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
volumes:
- name: www
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: chesterpvc通过以下命令应用,并验证
kubectl apply -f pvcpod.yaml
kubectl describe pod chesterpvcpod -n chesterns
kubectl describe pvc chesterpvc -n chesterns
kubectl describe pv chesterpv -n chesterns
curl 10.244.36.123/a.html回到顶部## 动态模式
动态模式可以解放集群管理员,集群管理员无须手工创建PV,而是通过StorageClass的设置对后端存储进行描述,标记为某种类型。此时要求PVC对存储的类型进行声明,系统将自动完成PV的创建及与PVC的绑定。PVC可以声明Class为"",说明该PVC禁止使用动态模式。
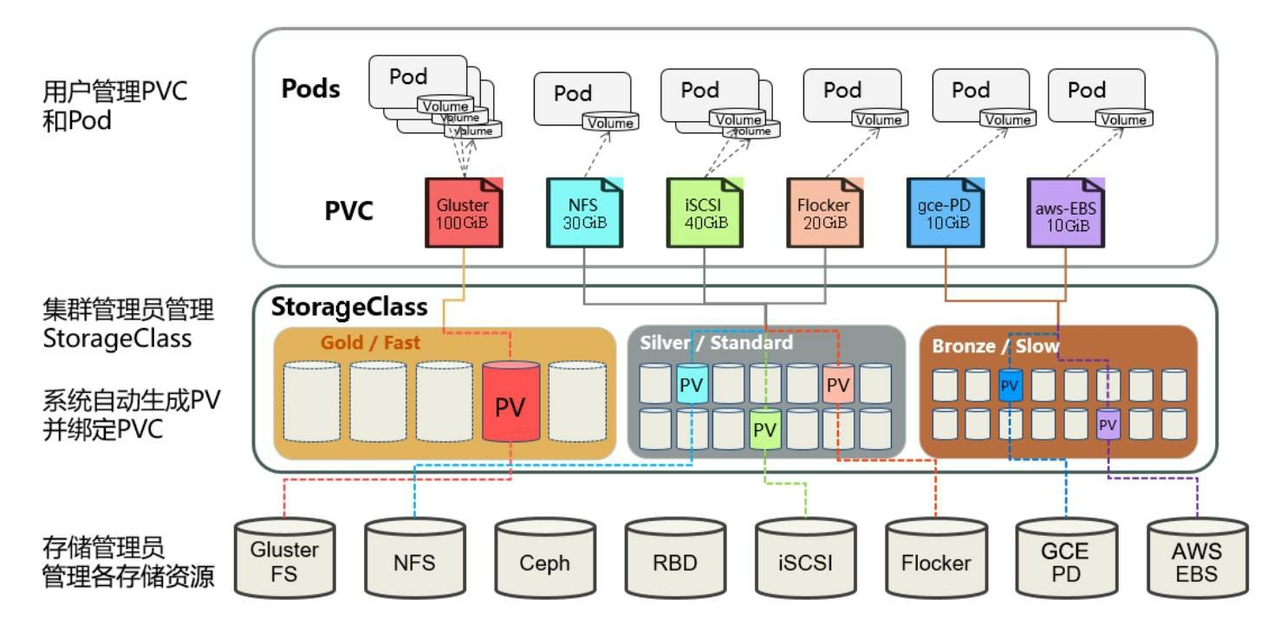
K8s需要安装插件支持NFS动态供给。
项目地址:https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner/tree/master/deploy
下载并安装,需要修改其中的namespace为我们自己的chesterns
kubectl apply -f nfs-rbac.yaml # 授权访问apiserver
kubectl apply -f nfs-deployment.yaml # 部署插件,需修改里面NFS服务器地址与共享目录
kubectl apply -f nfs-class.yaml # 创建存储类 下面我们定义pvc绑定我们刚建的storageclass,并且新建一个pod使用我们新建的这个pvc
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: chesterscpvc
namespace: chesterns
spec:
storageClassName: "nfs-client"
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: chesterpvcscpod
namespace: chesterns
spec:
containers:
- name: chesterpvcscpod
image: nginx
volumeMounts:
- name: nfs-pvc
mountPath: "/usr/share/nginx/html"
volumes:
- name: nfs-pvc
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: chesterscpvc验证
kubectl exec chesterpvcscpod -n chesterns -- touch /usr/share/nginx/html/aa
ll /tmp/chesternfs/回到顶部## ConfigMap
ConfigMap 是一种配置资源,用来将非机密性的数据保存到etcd键值对中。使用时,Pods可以将其用作环境变量、命令行参数或者存储卷中的配置文件。
下面就来实现一个简单的ConfigMap使用案例
定义ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: game-demo
namespace: chesterns
data:
# 类属性键;每一个键都映射到一个简单的值
player\_initial\_lives: "3"
ui\_properties\_file\_name: "user-interface.properties"
# 类文件键
game.properties: |
enemy.types=aliens,monsters
player.maximum-lives=5
user-interface.properties: |
color.good=purple
color.bad=yellow
allow.textmode=true 通过kubectl apply应用后,开始在pod中使用
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: configmap-demo-pod
namespace: chesterns
spec:
containers:
- name: demo
image: alpine
command: ["sleep", "3600"]
env:
# 定义环境变量
- name: PLAYER\_INITIAL\_LIVES # 请注意这里和 ConfigMap 中的键名是不一样的
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: game-demo # 这个值来自 ConfigMap
key: player\_initial\_lives # 需要取值的键
- name: UI\_PROPERTIES\_FILE\_NAME
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: game-demo
key: ui\_properties\_file\_name
volumeMounts:
- name: config
mountPath: "/config"
readOnly: true
volumes:
# 你可以在 Pod 级别设置卷,然后将其挂载到 Pod 内的容器中
- name: config
configMap:
# 提供你想要挂载的 ConfigMap 的名字
name: game-demo
# 来自 ConfigMap 的一组键,将被创建为文件
items:
- key: "game.properties"
path: "game.properties"
- key: "user-interface.properties"
path: "user-interface.properties"验证
kubectl apply -f configmap.yaml
kubectl apply -f configmappod.yaml回到顶部## Secret
Secret 类似于ConfigMap但专门用于保存机密数据。下面定义一个secret
apiVersion: v1
data:
username: YWRtaW4=
password: MWYyZDFlMmU2N2Rm
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: mysecret
namespace: chesterns应用secret
kubectl apply -f secret.yaml
kubectl get secret -n chesterns在Pod中使用Secret
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: mypod
namespace: chesterns
spec:
containers:
- name: mypod
image: redis
volumeMounts:
- name: foo
mountPath: "/etc/foo"
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: foo
secret:
secretName: mysecret验证
kubectl apply -f secretpod.yaml
kubectl get pod -n chesternskubectl exec mypod -n chesterns -- ls /etc/fooC#/.net/.net core QQ群:953553560


转载请注明:xuhss » K8S原来如此简单(七)存储