? 优质资源分享 ?
| 学习路线指引(点击解锁) | 知识定位 | 人群定位 |
|---|---|---|
| ? Python实战微信订餐小程序 ? | 进阶级 | 本课程是python flask+微信小程序的完美结合,从项目搭建到腾讯云部署上线,打造一个全栈订餐系统。 |
| ?Python量化交易实战? | 入门级 | 手把手带你打造一个易扩展、更安全、效率更高的量化交易系统 |
二值图像的细化算法也有很多种,比较有名的比如Hilditch细化、Rosenfeld细化、基于索引表的细化、还有Opencv自带的THINNING\_ZHANGSUEN、THINNING\_GUOHALL喜欢等等。这些都属于迭代的细化方式,当然还有一种是基于二值图像距离变换的细化方法,二值想比较,我个人认为是基于迭代的效果稳定、可靠,但是速度较慢,且速度和图片的内容有关,基于距离变换的版本,优点是速度稳定,但是效果差强人意。本文这里还是选择基于迭代的方式予以实现。
相关的参考文章有:[http://cgm.cs.mcgill.ca/~godfried/teaching/projects97/azar/skeleton.html](https://blog.csdn.net/biggbang) Hilditch细化https://blog.csdn.net/xiaotie/archive/2010/08/12/1797760.html 对Hilditch细化的改进版
http://cgm.cs.mcgill.ca/~godfried/teaching/projects97/azar/skeleton.html Rosenfeld细化
https://github.com/opencv/opencv_contrib/blob/4.x/modules/ximgproc/src/thinning.cpp Opencv的Zhang\guo细化
我们尝试的看下了Hilditch细化以及改进版本的Hilditch细化算法,发现其在某一个行的计算过程中,有着严重的前后依赖,非常不利于SIMD指令的并行化,这里我们优化了Opencv的两个算子。
一、原始方案
在上述的Opencv代码的链接中,以Zhang细化算法为例,其核心代码如下所示: if(thinningType == THINNING\_ZHANGSUEN){
for (int i = 1; i < img.rows-1; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j < img.cols-1; j++)
{
uchar p2 = img.at(i-1, j);
uchar p3 = img.at(i-1, j+1);
uchar p4 = img.at(i, j+1);
uchar p5 = img.at(i+1, j+1);
uchar p6 = img.at(i+1, j);
uchar p7 = img.at(i+1, j-1);
uchar p8 = img.at(i, j-1);
uchar p9 = img.at(i-1, j-1);
int A = (p2 == 0 && p3 == 1) + (p3 == 0 && p4 == 1) +
(p4 == 0 && p5 == 1) + (p5 == 0 && p6 == 1) +
(p6 == 0 && p7 == 1) + (p7 == 0 && p8 == 1) +
(p8 == 0 && p9 == 1) + (p9 == 0 && p2 == 1);
int B = p2 + p3 + p4 + p5 + p6 + p7 + p8 + p9;
int m1 = iter == 0 ? (p2 * p4 * p6) : (p2 * p4 * p8);
int m2 = iter == 0 ? (p4 * p6 * p8) : (p2 * p6 * p8);
if (A == 1 && (B >= 2 && B <= 6) && m1 == 0 && m2 == 0)
marker.at(i,j) = 1;
}
}
}非常之简洁啊,简洁的没有朋友,也没有效率的。 这样的代码其实只适合于新手学习算法的原理。无法用于实际的项目的。
可以明显的看出,A\B\m1\m2的判断并不要放在一起,而是可以分开,分开的话在很多的情况下后续的计算就可以不用做了,要知道,这是一个迭代的算法,而且通常要迭代几百次,因此,每一个迭代里能少一次计算量,整体下来的时间是非常可观的。
二、稍微改进版本
我们稍微做一个脱离Opencv版本的代码版本:
int IM\_Thinning\_Zhangsuen\_PureC(unsigned char *Src, unsigned char *Dest, int Width, int Height, int Stride)
{
int Channel = Stride / Width;
if ((Src == NULL) || (Dest == NULL)) return IM\_STATUS\_NULLREFRENCE;
if ((Width <= 0) || (Height <= 0)) return IM\_STATUS\_INVALIDPARAMETER;
if (Channel != 1) return IM\_STATUS\_INVALIDPARAMETER;
int Status = IM\_STATUS\_OK;
const int MaxIter = 2000;
unsigned char *Clone = (unsigned char *)calloc((Height + 2) * (Width + 2), sizeof(unsigned char));
unsigned short *IndexX = (unsigned short *)malloc(Width * Height / 4 * sizeof(unsigned short));
unsigned short *IndexY = (unsigned short *)malloc(Width * Height / 4 * sizeof(unsigned short));
if ((Clone == NULL) || (IndexX == NULL) || (IndexY == NULL))
{
Status = IM\_STATUS\_OUTOFMEMORY;
goto FreeMemory;
}
for (int Y = 0; Y < Height; Y++)
{
unsigned char *LinePS = Src + Y * Stride;
unsigned char *LinePD = Clone + (Y + 1) * (Width + 2) + 1;
for (int X = 0; X < Width; X++)
{
LinePD[X] = LinePS[X] & 1; // 全部量化为0和1两个数值
}
}
int Iter = 0;
while (true)
{
int Amount = 0;
for (int Y = 0; Y < Height; Y++)
{
unsigned char *LinePF = Clone + Y * (Width + 2) + 1;
unsigned char *LinePS = Clone + (Y + 1) * (Width + 2) + 1;
unsigned char *LinePT = Clone + (Y + 2) * (Width + 2) + 1;
for (int X = 0; X < Width; X++)
{
int P1 = LinePS[X];
if (P1 == 0) continue;
// P9 P2 P3
// P8 P1 P4
// P7 P6 P5
//
//int P9 = LinePF[X - 1];
//int P2 = LinePF[X];
//int P3 = LinePF[X + 1];
//int P8 = LinePS[X - 1];
//int P4 = LinePS[X + 1];
//int P7 = LinePT[X - 1];
//int P6 = LinePT[X];
//int P5 = LinePT[X + 1];
//int Sum = P2 + P3 + P4 + P5 + P6 + P7 + P8 + P9;
//if ((Sum < 2) || (Sum > 6)) continue;
int P2 = LinePF[X];
int P8 = LinePS[X - 1];
int P4 = LinePS[X + 1];
int P6 = LinePT[X];
int Sum = P2 + P8 + P4 + P6;
if (Sum == 4) continue;
int P3 = LinePF[X + 1];
int P9 = LinePF[X - 1];
int P5 = LinePT[X + 1];
int P7 = LinePT[X - 1];
Sum += P3 + P5 + P7 + P9;
if (Sum < 2) continue;
int Count = 0;
if ((P2 == 0) && (P3 == 1)) Count++;
if ((P3 == 0) && (P4 == 1)) Count++;
if ((P4 == 0) && (P5 == 1)) Count++;
if ((P5 == 0) && (P6 == 1)) Count++;
if ((P6 == 0) && (P7 == 1)) Count++;
if ((P7 == 0) && (P8 == 1)) Count++;
if ((P8 == 0) && (P9 == 1)) Count++;
if ((P9 == 0) && (P2 == 1)) Count++;
if ((Count == 1) && ((P2 & P4 & P6) == 0) && ((P4 & P6 & P8) == 0))
{
IndexX[Amount] = X;
IndexY[Amount] = Y;
Amount++;
}
}
}
if (Amount == 0) break;
for (int Y = 0; Y < Amount; Y++)
{
Clone[(IndexY[Y] + 1) * (Width + 2) + IndexX[Y] + 1] = 0;
}
Amount = 0;
for (int Y = 0; Y < Height; Y++)
{
// 后续的第二次循环,仅仅是几个变量判断不一样,自行添加
}
if (Amount == 0) break;
for (int Y = 0; Y < Amount; Y++)
{
Clone[(IndexY[Y] + 1) * (Width + 2) + IndexX[Y] + 1] = 0;
}
Iter++;
if (Iter >= MaxIter) break;
}
for (int Y = 0; Y < Height; Y++)
{
unsigned char *LinePD = Dest + Y * Stride;
unsigned char *LinePS = Clone + (Y + 1) * (Width + 2) + 1;
for (int X = 0; X < Width; X++)
{
LinePD[X] = LinePS[X] == 1 ? 255 : 0;
}
}
FreeMemory:
if (Clone != NULL) free(Clone);
if (IndexX != NULL) free(IndexX);
if (IndexY != NULL) free(IndexY);
return Status;
}几个方面的改进和改动:
1、使用了一个扩展边界的图像(高度和宽度在四周各扩散一个像素,类似于哨兵边界),用于减少每次取3*3领域时的边界判断。这个虽然占用了内存,但是可以很大的提高速度。
2、把A1\B\M的判断分开写,这样可以让有些循环提前退出,提高速度。
3、没有使用Vector,直接使用数组保存哪些需要改变值的位置(因为计算量小,对速度基本没有影响)。
4、对B的判断分了2步走,可以稍微提高下速度。我们选择下面这个测试图:

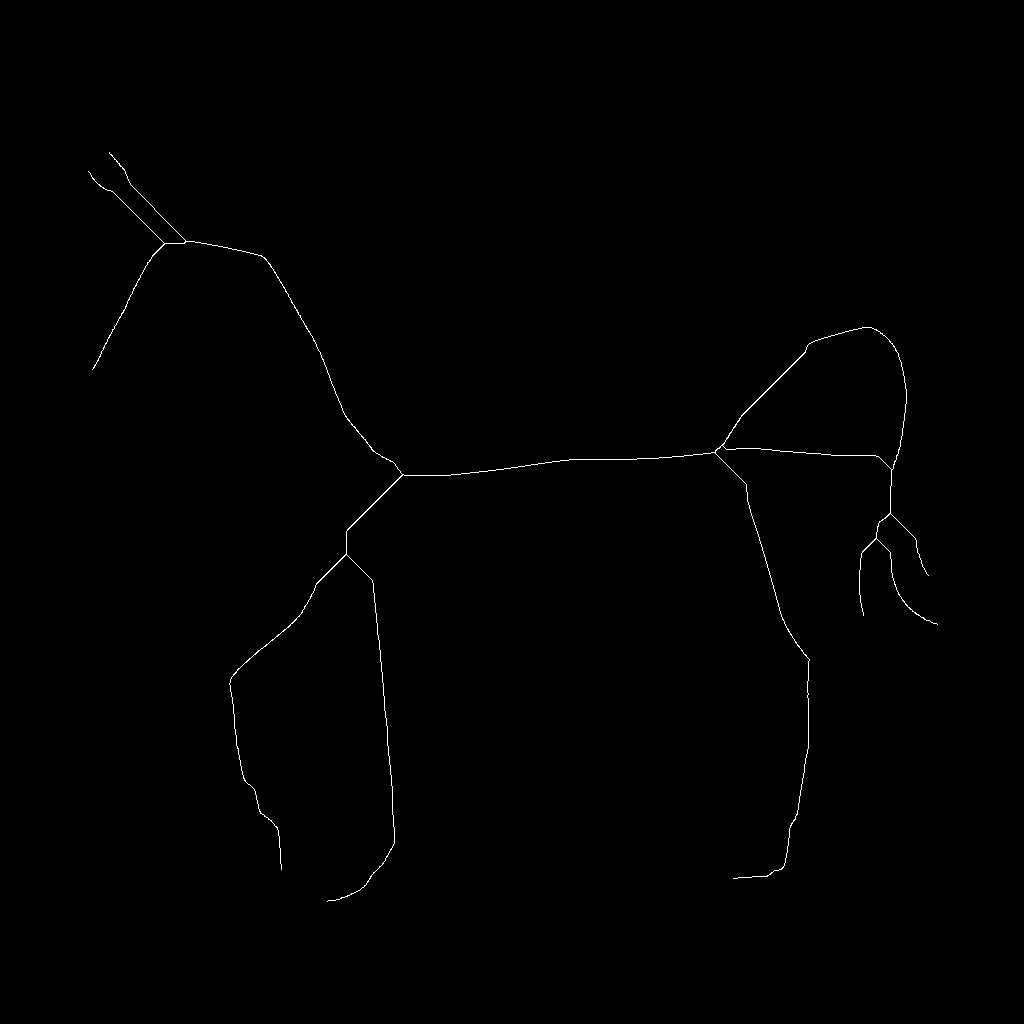
一副1024*1024大小的测试图,在我本机上上述测试代码的平均耗时大约是180ms,这个速度谈不上快。
三、再次改进版本
在我们进行SIMD优化前,我们还尝试了从算法层面上的另外一种优化。我们知道,在细化的算法中,本身已经是背景的像素是不要参与计算的,也就是上述代码中if (P1 == 0) continue; 的含义,那么如果没在迭代前,就算好了哪些部位不要计算,是不是迭代后就可以直接计算那些需要计算部分呢,这样就可以少了很多判断,虽然只是一个判断,但是在全图里如果有50%是背景,那就意味着要进行W*H/2判断的,再加上这个是在迭代里进行判断,计算量也是相当可观的。
这个事先计算好哪些是前景的工作,针对二值图像,其实就是类似于传统的RLE行程编码,我们计算出每行前景的起点终点,等等。这个算法大家自行去研究。
如果在每次迭代前都进行这个RLE行程编码,那也会带来新的问题,因为行程编码也是全图处理,也是一个需要时间的工作,那这样后续带来的速度优化反而会被行程编码给抵消甚至导致减速。但是,如果只进行迭代前的一次编码,随着迭代的进行,更多的像素被判定为背景,之前计算的行程编码里已经有很多是不需要计算的了, 为了解决这个矛盾,一个建议的处理方法就是,每个若干次迭代,更新下行程编码的结果,比如20次或者50次,这样的话,即不会因为行程编码的耗时影响整体速度,又在一定程度上逐次的减少了计算量。
相关代码如下所示:
int IM\_Thinning\_Zhangsuen\_PureC\_Opt(unsigned char *Src, unsigned char *Dest, int Width, int Height, int Stride)
{
int Channel = Stride / Width;
if ((Src == NULL) || (Dest == NULL)) return IM\_STATUS\_NULLREFRENCE;
if ((Width <= 0) || (Height <= 0)) return IM\_STATUS\_INVALIDPARAMETER;
if (Channel != 1) return IM\_STATUS\_INVALIDPARAMETER;
int Status = IM\_STATUS\_OK;
const int MaxIter = 2000;
unsigned char *Clone = (unsigned char *)calloc((Height + 2) * (Width + 2), sizeof(unsigned char));
unsigned short *IndexX = (unsigned short *)malloc(Width * Height / 4 * sizeof(unsigned short));
unsigned short *IndexY = (unsigned short *)malloc(Width * Height / 4 * sizeof(unsigned short));
RLE\_Line *RL\_H = (RLE\_Line *)malloc((Height + 2) * sizeof(RLE\_Line));
if ((Clone == NULL) || (IndexX == NULL) || (IndexY == NULL) || (RL\_H == NULL))
{
Status = IM\_STATUS\_OUTOFMEMORY;
goto FreeMemory;
}
for (int Y = 0; Y < Height; Y++)
{
unsigned char *LinePS = Src + Y * Stride;
unsigned char *LinePD = Clone + (Y + 1) * (Width + 2) + 1;
for (int X = 0; X < Width; X++)
{
LinePD[X] = LinePS[X] & 1;
}
}
Status = IM\_GetMaskRLE\_Hori(Clone, Width + 2, Height + 2, Width + 2, RL\_H);
if (Status != IM\_STATUS\_OK) goto FreeMemory;
int Iter = 0;
while (true)
{
if (Iter % 50 == 0) // 每迭代50次更细一下
{
for (int Z = 0; Z < Height + 2; Z++)
{
if ((RL\_H[Z].Amount != 0) && (RL\_H[Z].SE != NULL)) free(RL\_H[Z].SE);
}
Status = IM\_GetMaskRLE\_Hori(Clone, Width + 2, Height + 2, Width + 2, RL\_H);
}
int Amount = 0;
for (int Y = 0; Y < Height; Y++)
{
unsigned char *LinePF = Clone + Y * (Width + 2) + 1;
unsigned char *LinePS = Clone + (Y + 1) * (Width + 2) + 1;
unsigned char *LinePT = Clone + (Y + 2) * (Width + 2) + 1;
for (int K = 0; K < RL\_H[Y + 1].Amount; K++)
{
for (int X = RL\_H[Y + 1].SE[K].Start - 1 ; X <= RL\_H[Y + 1].SE[K].End - 1; X++)
{
int P1 = LinePS[X];
if (P1 == 0) continue;
// P9 P2 P3
// P8 P1 P4
// P7 P6 P5 // 条件3:至少有两个是前景点
int P2 = LinePF[X];
int P8 = LinePS[X - 1];
int P4 = LinePS[X + 1];
int P6 = LinePT[X];
int Sum = P2 + P8 + P4 + P6;
if (Sum == 4) continue; // 条件2: P1,P3,P5,P7不全部为前景点
int P3 = LinePF[X + 1];
int P9 = LinePF[X - 1];
int P5 = LinePT[X + 1];
int P7 = LinePT[X - 1]; // 以方便计算8连通联结数。
Sum += P3 + P5 + P7 + P9;
if (Sum < 2) continue; // 条件3:至少有两个是前景点
int Count = 0;
if ((P2 == 0) && (P3 == 1)) Count++;
if ((P3 == 0) && (P4 == 1)) Count++;
if ((P4 == 0) && (P5 == 1)) Count++;
if ((P5 == 0) && (P6 == 1)) Count++;
if ((P6 == 0) && (P7 == 1)) Count++;
if ((P7 == 0) && (P8 == 1)) Count++;
if ((P8 == 0) && (P9 == 1)) Count++;
if ((P9 == 0) && (P2 == 1)) Count++;
if ((Count == 1) && ((P2 & P4 & P6) == 0) && ((P4 & P6 & P8) == 0))
{
IndexX[Amount] = X;
IndexY[Amount] = Y;
Amount++;
}
}
}
}
if (Amount == 0) break;
for (int Y = 0; Y < Amount; Y++)
{
Clone[(IndexY[Y] + 1) * (Width + 2) + IndexX[Y] + 1] = 0;
}
Amount = 0;
for (int Y = 0; Y < Height; Y++)
{
// 后续的第二次循环,自行添加
}
if (Amount == 0) break;
for (int Y = 0; Y < Amount; Y++)
{
Clone[(IndexY[Y] + 1) * (Width + 2) + IndexX[Y] + 1] = 0;
}
Iter++;
if (Iter >= MaxIter) break;
}
for (int Y = 0; Y < Height; Y++)
{
unsigned char *LinePD = Dest + Y * Stride;
unsigned char *LinePS = Clone + (Y + 1) * (Width + 2) + 1;
for (int X = 0; X < Width; X++)
{
LinePD[X] = LinePS[X] == 1 ? 255 : 0;
}
}
FreeMemory:
if (Clone != NULL) free(Clone);
if (IndexX != NULL) free(IndexX);
if (IndexY != NULL) free(IndexY);
if (RL\_H != NULL)
{
for (int Z = 0; Z < Height + 2; Z++)
{
if ((RL\_H[Z].Amount != 0) && (RL\_H[Z].SE != NULL)) free(RL\_H[Z].SE);
}
free(RL\_H);
}
return Status;
}同样的图像,速度可以提高到55ms,有将近3倍额速度提高。
不过这里的提速比例不是很固定的,对于不同的类型的图像结果不禁相同,对于那些有大块连续的二值图,提速就越明显,而对于毫无规律的随机图,可能就不是很明显了。
四、SSE改进版本
上述改进版本还可以通过SIMD指令进一步优化,类似于我在Sobel优化里使用的方法,我们一次性加载16个字节以及他周边的8个位置连续的16个字节,但是核心的技巧在于如何实现那些分支预测,特别是continue。
因为一次性加载了16个像素,在利用了行程编码后,案例说这16个字节都是需要进行处理的目标,但是由于前述不是每次迭代都要更新行程编码的缘故,总会有部分是无效像素,也有可能是全部的无效像素,因此,我们处理的代码中就可能同时存在前景和背景,但是对于背景我们是不需要处理的,而前景像素也有可能在中间条件判断时退出循环,但是对于SIMD质量来说,他无法局部退出,要么大家一起计算,要么大家一起退出,因此,我们必须将须有的计算都完成,而不能提前退出,但是有一点特殊的就是,如果所有的像素都已经满足了某个提提前退出的条件,那也是可以退出的。
因为我们知道,在每次迭代时,对于前景中哪些大块的范围,其中间的区域都是不满足要改变的条件的,也就是说在上面的 if (Sum == 4) continue; if (Sum \_\_m128i P1 = \_mm\_loadu\_si128((\_\_m128i *)(LinePS + X));
\_\_m128i FlagA = \_mm\_cmpeq\_epi8(P1, \_mm\_setzero\_si128()); // 全部为0,退出
if (\_mm\_movemask\_epi8(FlagA) == 65535) continue;
\_\_m128i Flag = \_mm\_andnot\_si128(FlagA, \_mm\_set1\_epi8(255)); // 记录下那些是不为0的
\_\_m128i P2 = \_mm\_loadu\_si128((\_\_m128i *)(LinePF + X + 0));
\_\_m128i P8 = \_mm\_loadu\_si128((\_\_m128i *)(LinePS + X - 1));
\_\_m128i P4 = \_mm\_loadu\_si128((\_\_m128i *)(LinePS + X + 1));
\_\_m128i P6 = \_mm\_loadu\_si128((\_\_m128i *)(LinePT + X + 0));
\_\_m128i Sum = \_mm\_add\_epi8(\_mm\_add\_epi8(P2, P4), \_mm\_add\_epi8(P6, P8));
\_\_m128i FlagB = \_mm\_cmpeq\_epi8(Sum, \_mm\_set1\_epi8(4));
if (\_mm\_movemask\_epi8(FlagB) == 65535) continue; // 全部都等于4,退出
Flag = \_mm\_andnot\_si128(FlagB, Flag); // 记录下那些不为0,且Sum不等于4的
\_\_m128i P9 = \_mm\_loadu\_si128((\_\_m128i *)(LinePF + X - 1));
\_\_m128i P3 = \_mm\_loadu\_si128((\_\_m128i *)(LinePF + X + 1));
\_\_m128i P7 = \_mm\_loadu\_si128((\_\_m128i *)(LinePT + X - 1));
\_\_m128i P5 = \_mm\_loadu\_si128((\_\_m128i *)(LinePT + X + 1));
Sum = \_mm\_add\_epi8(Sum, \_mm\_add\_epi8(\_mm\_add\_epi8(P9, P3), \_mm\_add\_epi8(P7, P5)));
\_\_m128i FlagC = \_mm\_cmplt\_epi8(Sum, \_mm\_set1\_epi8(2));
if (\_mm\_movemask\_epi8(FlagC) == 65535) continue; // 全部都小于2,退出
Flag = \_mm\_andnot\_si128(FlagC, Flag); // 记录下那些不为0,且Sum不等于4的,后续的Sum小于2的
\_\_m128i Count = \_mm\_setzero\_si128();
Count = \_mm\_sub\_epi8(Count, \_mm\_and\_si128(\_mm\_cmpeq\_epi8(P2, Zero), \_mm\_cmpeq\_epi8(P3, One)));
Count = \_mm\_sub\_epi8(Count, \_mm\_and\_si128(\_mm\_cmpeq\_epi8(P3, Zero), \_mm\_cmpeq\_epi8(P4, One)));
Count = \_mm\_sub\_epi8(Count, \_mm\_and\_si128(\_mm\_cmpeq\_epi8(P4, Zero), \_mm\_cmpeq\_epi8(P5, One)));
Count = \_mm\_sub\_epi8(Count, \_mm\_and\_si128(\_mm\_cmpeq\_epi8(P5, Zero), \_mm\_cmpeq\_epi8(P6, One)));
Count = \_mm\_sub\_epi8(Count, \_mm\_and\_si128(\_mm\_cmpeq\_epi8(P6, Zero), \_mm\_cmpeq\_epi8(P7, One)));
Count = \_mm\_sub\_epi8(Count, \_mm\_and\_si128(\_mm\_cmpeq\_epi8(P7, Zero), \_mm\_cmpeq\_epi8(P8, One)));
Count = \_mm\_sub\_epi8(Count, \_mm\_and\_si128(\_mm\_cmpeq\_epi8(P8, Zero), \_mm\_cmpeq\_epi8(P9, One)));
Count = \_mm\_sub\_epi8(Count, \_mm\_and\_si128(\_mm\_cmpeq\_epi8(P9, Zero), \_mm\_cmpeq\_epi8(P2, One)));
\_\_m128i P246 = \_mm\_and\_si128(\_mm\_and\_si128(P2, P4), P6);
\_\_m128i P468 = \_mm\_and\_si128(\_mm\_and\_si128(P4, P6), P8);
\_\_m128i FlagD = \_mm\_and\_si128(\_mm\_cmpeq\_epi8(Count, One), \_mm\_and\_si128(\_mm\_cmpeq\_epi8(P246, Zero), \_mm\_cmpeq\_epi8(P468, Zero)));
if (\_mm\_movemask\_epi8(FlagD) == 0) continue;
Flag = \_mm\_and\_si128(FlagD, Flag);
// 用Flag.m128i\_u8或者写入到一个临时数组里速度没啥区别
if (\_mm\_extract\_epi8(Flag, 0) == 255)
{
IndexX[Amount] = X + 0;
IndexY[Amount] = Y;
Amount++;
} if (\_mm\_extract\_epi8(Flag, 1) == 255)
{
IndexX[Amount] = X + 1;
IndexY[Amount] = Y;
Amount++;
} /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////上面的细节有几个地方值的学习。
第一、_mm_movemask_epi8的使用,这个我在很多场合下都提过,可用于批量判断一个SIMD寄存器里的状态。本例只用他做判断是否SSE寄存器都符合某一个指标。
第二、Flag 变量的作用,Flag用于来记录下满足所有条件的像素,这样才能知道经过多个判断后最终还剩下那些像素需要真正的处理。其中\_mm\_andnot\_si128也是一个灵活的应用。第三、if ((P2 == 0) && (P3 == 1)) Count++; 这样的语句如果直接翻译到SSE代码,是比较麻烦的(可以使用_mm_blendv_si128),我这里巧妙的使用了u8和i8数据类型的特点,u8的255就对应了i8的-1,0还是对应0,然后加法就可以变为减法了。
第四、填写IndeX和IndexY的过程确实是无法用SIMD指令实现的,这里只能去拆解SIMD变量,这个有几个方法,一个就是用想本例中直接使用_mm_extract_epi8,另外一种方式可以是使用SIMD变量的m128i_u8成员,但是这个有可能对性能有所影响。
使用SIMD优化后,上述相同的图片大概耗时在28ms左右,速度有进一步的提高。
五、其他说明
虽然较原始版本速度有较大的提高,但是和商业软件相比,还是有很大的差距,人家halcon这个图用时5ms,直接悲剧。
至少目前从公开的资料中还没有看到halcon所用的算法的为什么这么快,待有缘了在研究这个算法吧。
另外,halcon的计算结果和opencv的GulHALL的结果比较类似,但是那个算法要比Zhang还要慢。
当然,CV自带的这两个算法是可以并行的,当然这里的必行是指迭代内部的并行,而不是迭代之间的并行,但是由于每次迭代的计算量相对于来说比较小,这种并行对CPU级别的线程来说是不太划算的,但是GPU级别的还是很友好的。不过HALONC这个算法可没有用GPU哦。
测试Demo: Zhang 以及 Guo 图像细化
如果想时刻关注本人的最新文章,也可关注公众号或者添加本人微信: laviewpbt
